"""Example: Optimize yaw and compare AEP
This example demonstrates how to perform a yaw optimization and evaluate the performance
over a full wind rose.
The script performs the following steps:
1. Load a wind rose from a csv file
2. Calculates the optimal yaw angles for a wind speed of 8 m/s across the directions
3. Applies the optimal yaw angles to the wind rose and calculates the AEP
"""
from time import perf_counter as timerpc
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from floris import (
FlorisModel,
TimeSeries,
WindRose,
)
from floris.optimization.yaw_optimization.yaw_optimizer_sr import YawOptimizationSR
# Load the wind rose from csv
wind_rose = WindRose.read_csv_long(
"../inputs/wind_rose.csv", wd_col="wd", ws_col="ws", freq_col="freq_val", ti_col_or_value=0.06
)
# Load FLORIS
fmodel = FlorisModel("../inputs/gch.yaml")
# Specify wind farm layout and update in the floris object
N = 2 # number of turbines per row and per column
X, Y = np.meshgrid(
5.0 * fmodel.core.farm.rotor_diameters_sorted[0][0] * np.arange(0, N, 1),
5.0 * fmodel.core.farm.rotor_diameters_sorted[0][0] * np.arange(0, N, 1),
)
fmodel.set(layout_x=X.flatten(), layout_y=Y.flatten())
# Get the number of turbines
n_turbines = len(fmodel.layout_x)
# Optimize the yaw angles. This could be done for every wind direction and wind speed
# but in practice it is much faster to optimize only for one speed and infer the rest
# using a rule of thumb
time_series = TimeSeries(
wind_directions=wind_rose.wind_directions, wind_speeds=8.0, turbulence_intensities=0.06
)
fmodel.set(wind_data=time_series)
# Get the optimal angles
start_time = timerpc()
yaw_opt = YawOptimizationSR(
fmodel=fmodel,
minimum_yaw_angle=0.0, # Allowable yaw angles lower bound
maximum_yaw_angle=20.0, # Allowable yaw angles upper bound
Ny_passes=[5, 4],
exclude_downstream_turbines=True,
)
df_opt = yaw_opt.optimize()
end_time = timerpc()
t_tot = end_time - start_time
print(f"Optimization finished in {t_tot:.2f} seconds.")
# Calculate the AEP in the baseline case
fmodel.set(wind_data=wind_rose)
fmodel.run()
farm_power_baseline = fmodel.get_farm_power()
aep_baseline = fmodel.get_farm_AEP()
# Now need to apply the optimal yaw angles to the wind rose to get the optimized AEP
# do this by applying a rule of thumb where the optimal yaw is applied between 6 and 12 m/s
# and ramped down to 0 above and below this range
# Grab wind speeds and wind directions from the fmodel. Note that we do this because the
# yaw angles will need to be n_findex long, and accounting for the fact that some wind
# directions and wind speeds may not be present in the wind rose (0 frequency) and aren't
# included in the fmodel
wind_directions = fmodel.wind_directions
wind_speeds = fmodel.wind_speeds
n_findex = fmodel.n_findex
# Now define how the optimal yaw angles for 8 m/s are applied over the other wind speeds
yaw_angles_opt = np.vstack(df_opt["yaw_angles_opt"])
yaw_angles_wind_rose = np.zeros((n_findex, n_turbines))
for i in range(n_findex):
wind_speed = wind_speeds[i]
wind_direction = wind_directions[i]
# Interpolate the optimal yaw angles for this wind direction from df_opt
id_opt = df_opt["wind_direction"] == wind_direction
yaw_opt_full = np.array(df_opt.loc[id_opt, "yaw_angles_opt"])[0]
# Now decide what to do for different wind speeds
wind_speed_low_no_steer = 4.0
wind_speed_high_no_steer = 14.0
wind_speed_low_steer = 6.0
wind_speed_high_steer = 12.0
if (wind_speed < wind_speed_low_no_steer) | (wind_speed > wind_speed_high_no_steer):
yaw_opt = np.zeros(n_turbines) # do nothing for very low/high speeds
elif wind_speed < wind_speed_low_steer:
yaw_opt = (
yaw_opt_full
* (wind_speed_low_steer - wind_speed)
/ (wind_speed_low_steer - wind_speed_low_no_steer)
) # Linear ramp up
elif wind_speed > wind_speed_high_steer:
yaw_opt = (
yaw_opt_full
* (wind_speed_high_no_steer - wind_speed)
/ (wind_speed_high_no_steer - wind_speed_high_steer)
) # Linear ramp down
else:
yaw_opt = yaw_opt_full # Apply full offsets between 6.0 and 12.0 m/s
# Save to collective array
yaw_angles_wind_rose[i, :] = yaw_opt
# Now apply the optimal yaw angles and get the AEP
fmodel.set(yaw_angles=yaw_angles_wind_rose)
fmodel.run()
aep_opt = fmodel.get_farm_AEP()
aep_uplift = 100.0 * (aep_opt / aep_baseline - 1)
farm_power_opt = fmodel.get_farm_power()
print(f"Baseline AEP: {aep_baseline / 1e9:.2f} GWh.")
print(f"Optimal AEP: {aep_opt / 1e9:.2f} GWh.")
print(f"Relative AEP uplift by wake steering: {aep_uplift:.3f} %.")
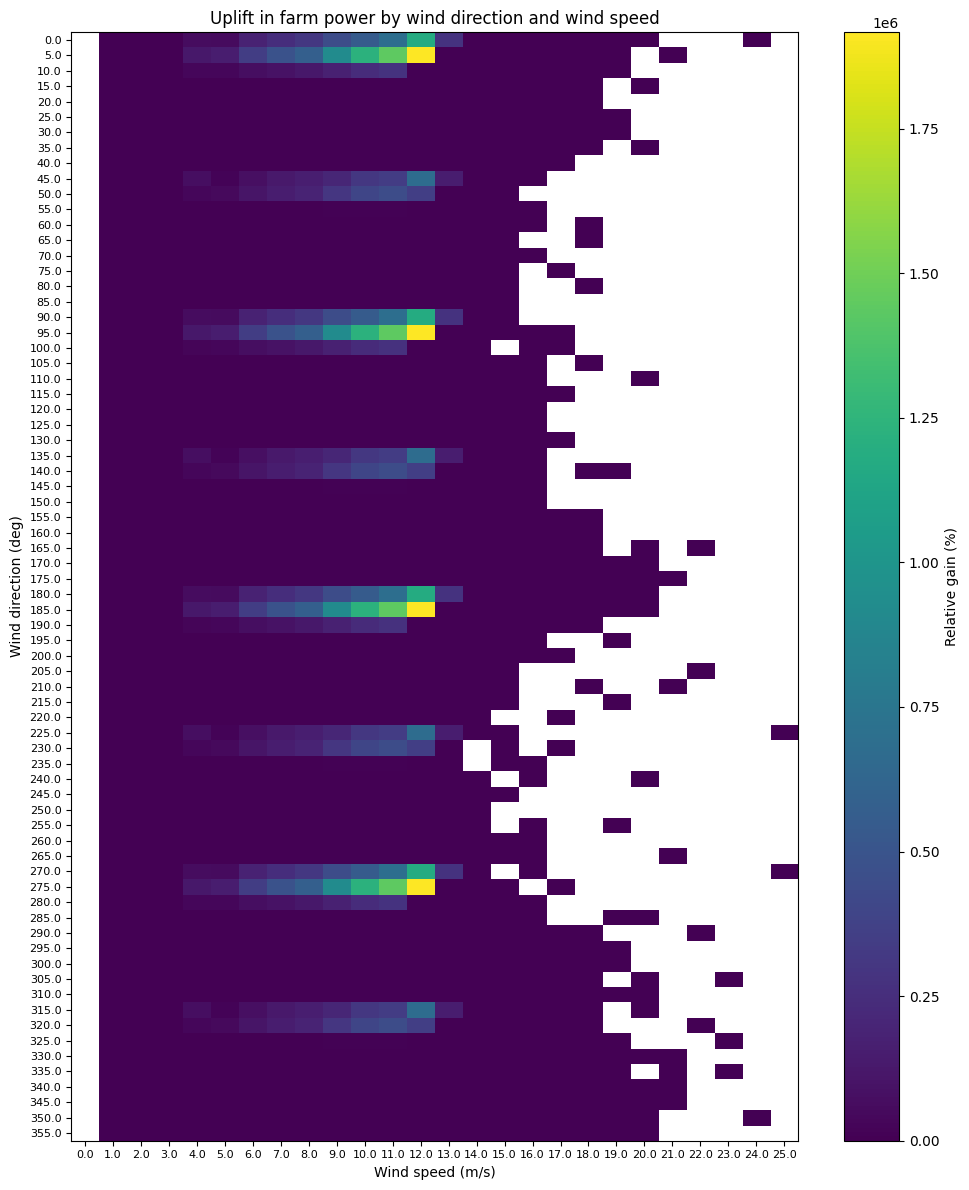
# Use farm_power_baseline, farm_power_opt and wind_data to make a heat map of uplift by
# wind direction and wind speed
wind_directions = wind_rose.wind_directions
wind_speeds = wind_rose.wind_speeds
relative_gain = farm_power_opt - farm_power_baseline
# Plot the heatmap with wind speeds on x, wind directions on y and relative gain as the color
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 12))
cax = ax.imshow(relative_gain, cmap="viridis", aspect="auto")
fig.colorbar(cax, ax=ax, label="Relative gain (%)")
ax.set_yticks(np.arange(len(wind_directions)))
ax.set_yticklabels(wind_directions)
ax.set_xticks(np.arange(len(wind_speeds)))
ax.set_xticklabels(wind_speeds)
ax.set_ylabel("Wind direction (deg)")
ax.set_xlabel("Wind speed (m/s)")
# Reduce x and y tick font size
for tick in ax.yaxis.get_major_ticks():
tick.label1.set_fontsize(8)
for tick in ax.xaxis.get_major_ticks():
tick.label1.set_fontsize(8)
# Set y ticks to be horizontal
for tick in ax.get_yticklabels():
tick.set_rotation(0)
ax.set_title("Uplift in farm power by wind direction and wind speed", fontsize=12)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')