"""Example: Helix active wake mixing
Example to test out using helix wake mixing of upstream turbines.
Helix wake mixing is turned on at turbine 1, off at turbines 2 to 4;
Turbine 2 is in wake turbine 1, turbine 4 in wake of turbine 3.
"""
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import yaml
import floris.flow_visualization as flowviz
from floris import FlorisModel
# Grab model of FLORIS and update to awc-enabled turbines
fmodel = FlorisModel("../inputs/emgauss_helix.yaml")
fmodel.set_operation_model("awc")
# Set the wind directions and speeds to be constant over N different helix amplitudes
N = 1
awc_modes = np.array(["helix", "baseline", "baseline", "baseline"]).reshape(4, N).T
awc_amplitudes = np.array([2.5, 0, 0, 0]).reshape(4, N).T
# Create 4 WT WF layout with lateral offset of 3D and streamwise offset of 4D
D = 240
fmodel.set(
layout_x=[0.0, 4*D, 0.0, 4*D],
layout_y=[0.0, 0.0, -3*D, -3*D],
wind_directions=270 * np.ones(N),
wind_speeds=8.0 * np.ones(N),
turbulence_intensities=0.06*np.ones(N),
awc_modes=awc_modes,
awc_amplitudes=awc_amplitudes
)
fmodel.run()
turbine_powers = fmodel.get_turbine_powers()
# Plot the flow fields for T1 awc_amplitude = 2.5
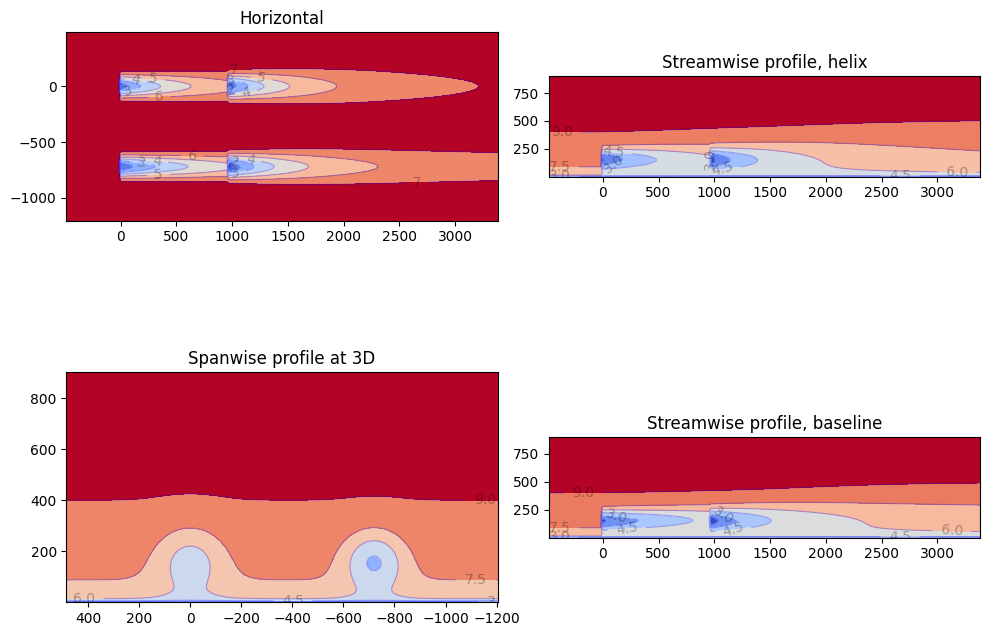
horizontal_plane = fmodel.calculate_horizontal_plane(
x_resolution=200,
y_resolution=100,
height=150.0,
)
y_plane_baseline = fmodel.calculate_y_plane(
x_resolution=200,
z_resolution=100,
crossstream_dist=0.0,
)
y_plane_helix = fmodel.calculate_y_plane(
x_resolution=200,
z_resolution=100,
crossstream_dist=-3*D,
)
cross_plane = fmodel.calculate_cross_plane(
y_resolution=100,
z_resolution=100,
downstream_dist=720.0,
)
# Create the plots
fig, ax_list = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(10, 8), tight_layout=True)
ax_list = ax_list.flatten()
flowviz.visualize_cut_plane(
horizontal_plane,
ax=ax_list[0],
label_contours=True,
title="Horizontal"
)
flowviz.visualize_cut_plane(
cross_plane,
ax=ax_list[2],
label_contours=True,
title="Spanwise profile at 3D"
)
# fig2, ax_list2 = plt.subplots(2, 1, figsize=(10, 8), tight_layout=True)
# ax_list2 = ax_list2.flatten()
flowviz.visualize_cut_plane(
y_plane_baseline,
ax=ax_list[1],
label_contours=True,
title="Streamwise profile, helix"
)
flowviz.visualize_cut_plane(
y_plane_helix,
ax=ax_list[3],
label_contours=True,
title="Streamwise profile, baseline"
)
# Calculate the effect of changing awc_amplitudes
N = 50
awc_amplitudes = np.array([
np.linspace(0, 5, N),
np.zeros(N), np.zeros(N), np.zeros(N)
]).reshape(4, N).T
awc_modes = np.tile(awc_modes, (N,1)) # Repeat over N findices
# Reset FlorisModel for different helix amplitudes
fmodel.set(
wind_directions=270 * np.ones(N),
wind_speeds=8 * np.ones(N),
turbulence_intensities=0.06*np.ones(N),
awc_modes=awc_modes,
awc_amplitudes=awc_amplitudes
)
fmodel.run()
turbine_powers = fmodel.get_turbine_powers()
# Plot the power as a function of helix amplitude
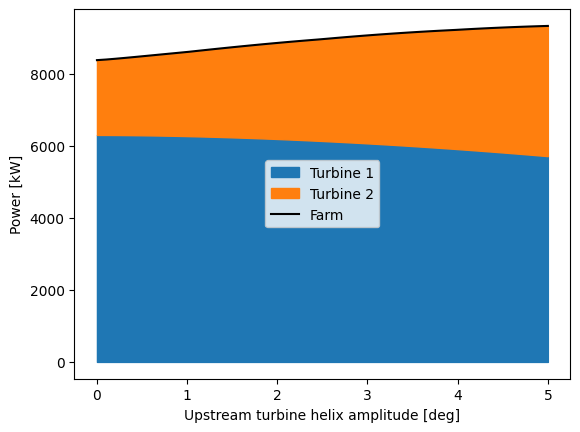
fig_power, ax_power = plt.subplots()
ax_power.fill_between(
awc_amplitudes[:, 0],
0,
turbine_powers[:, 0]/1000,
color='C0',
label='Turbine 1'
)
ax_power.fill_between(
awc_amplitudes[:, 0],
turbine_powers[:, 0]/1000,
turbine_powers[:, :2].sum(axis=1)/1000,
color='C1',
label='Turbine 2'
)
ax_power.plot(
awc_amplitudes[:, 0],
turbine_powers[:,:2].sum(axis=1)/1000,
color='k',
label='Farm'
)
ax_power.set_xlabel("Upstream turbine helix amplitude [deg]")
ax_power.set_ylabel("Power [kW]")
ax_power.legend()
flowviz.show()
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')