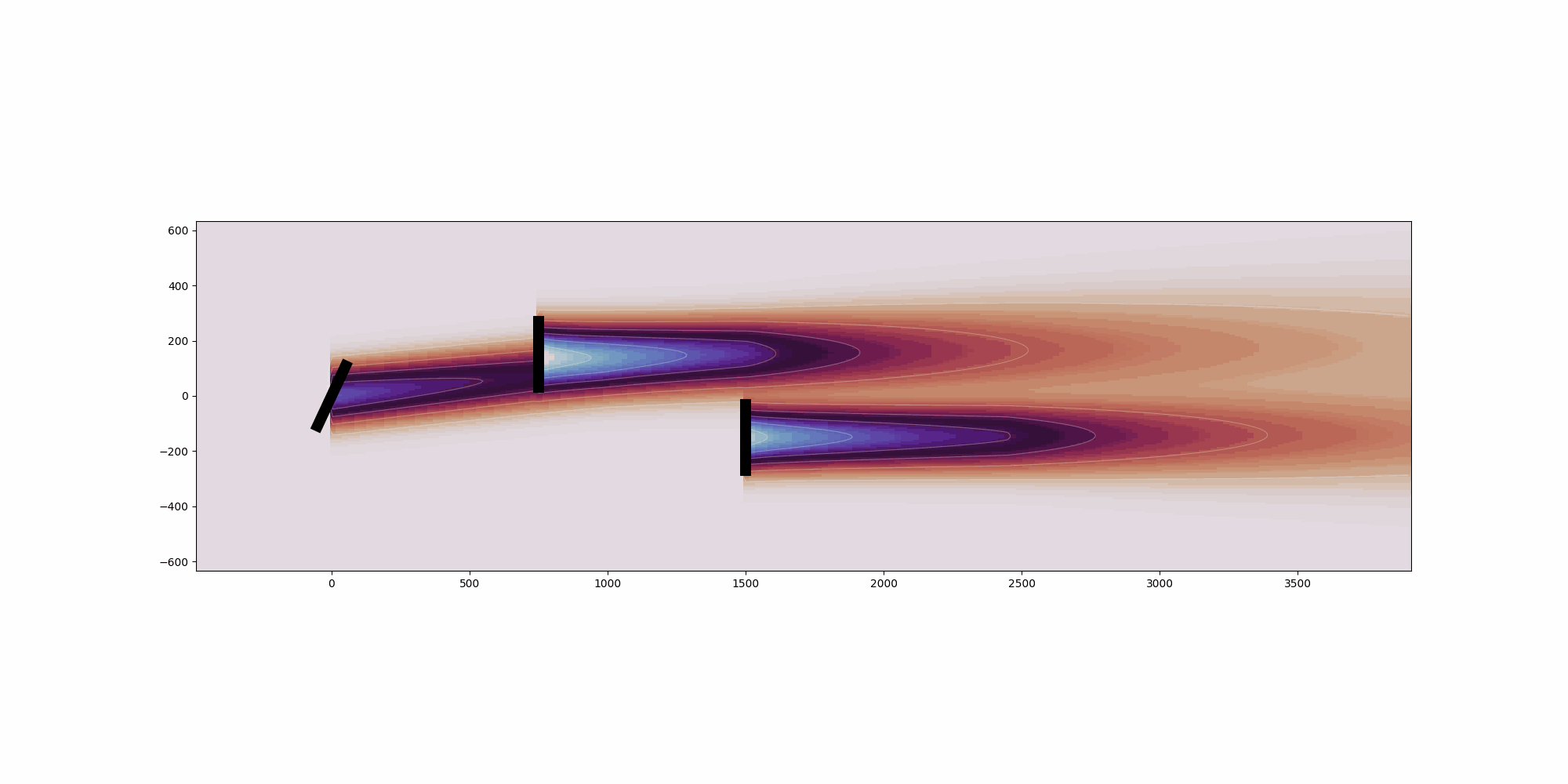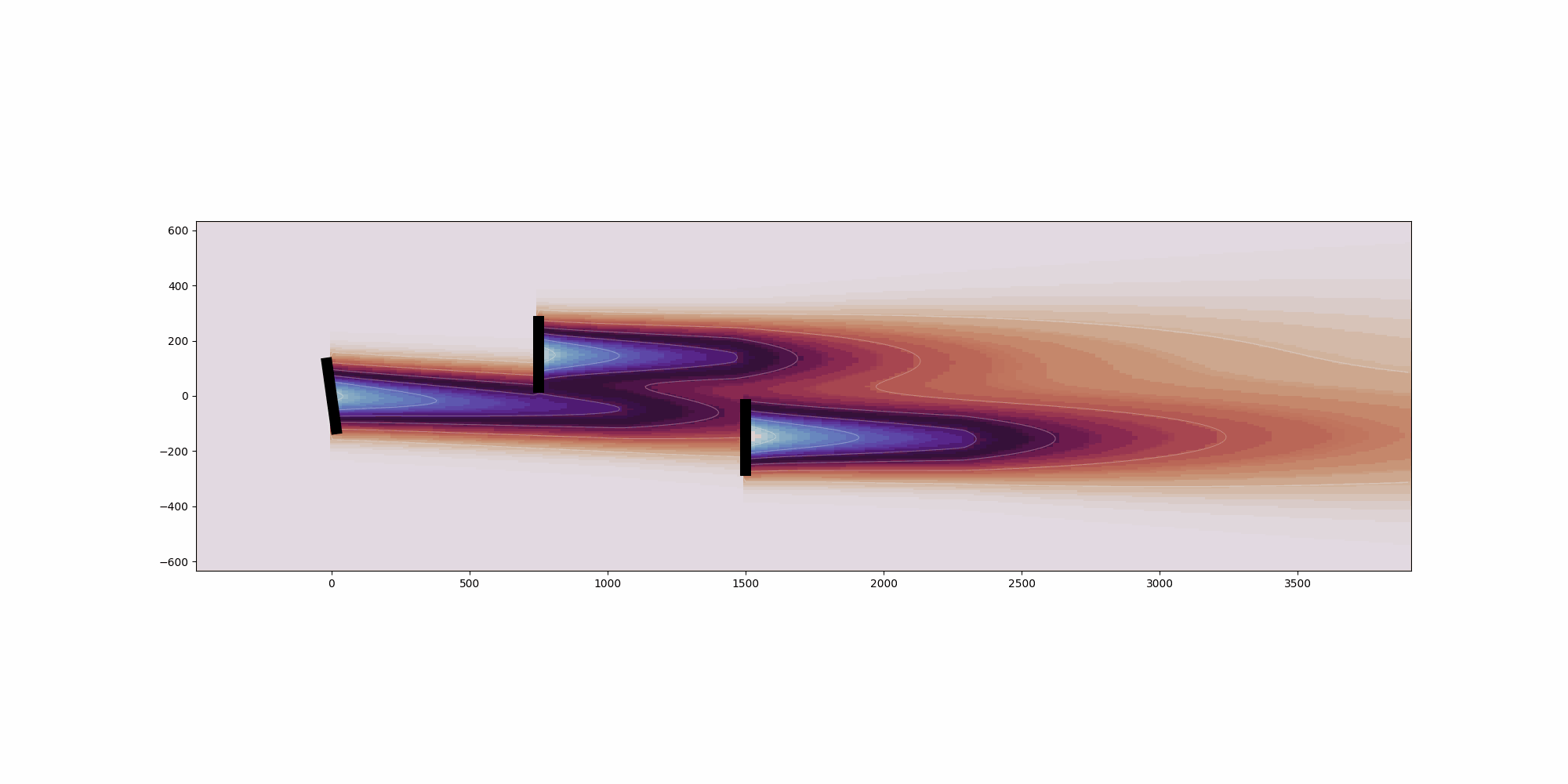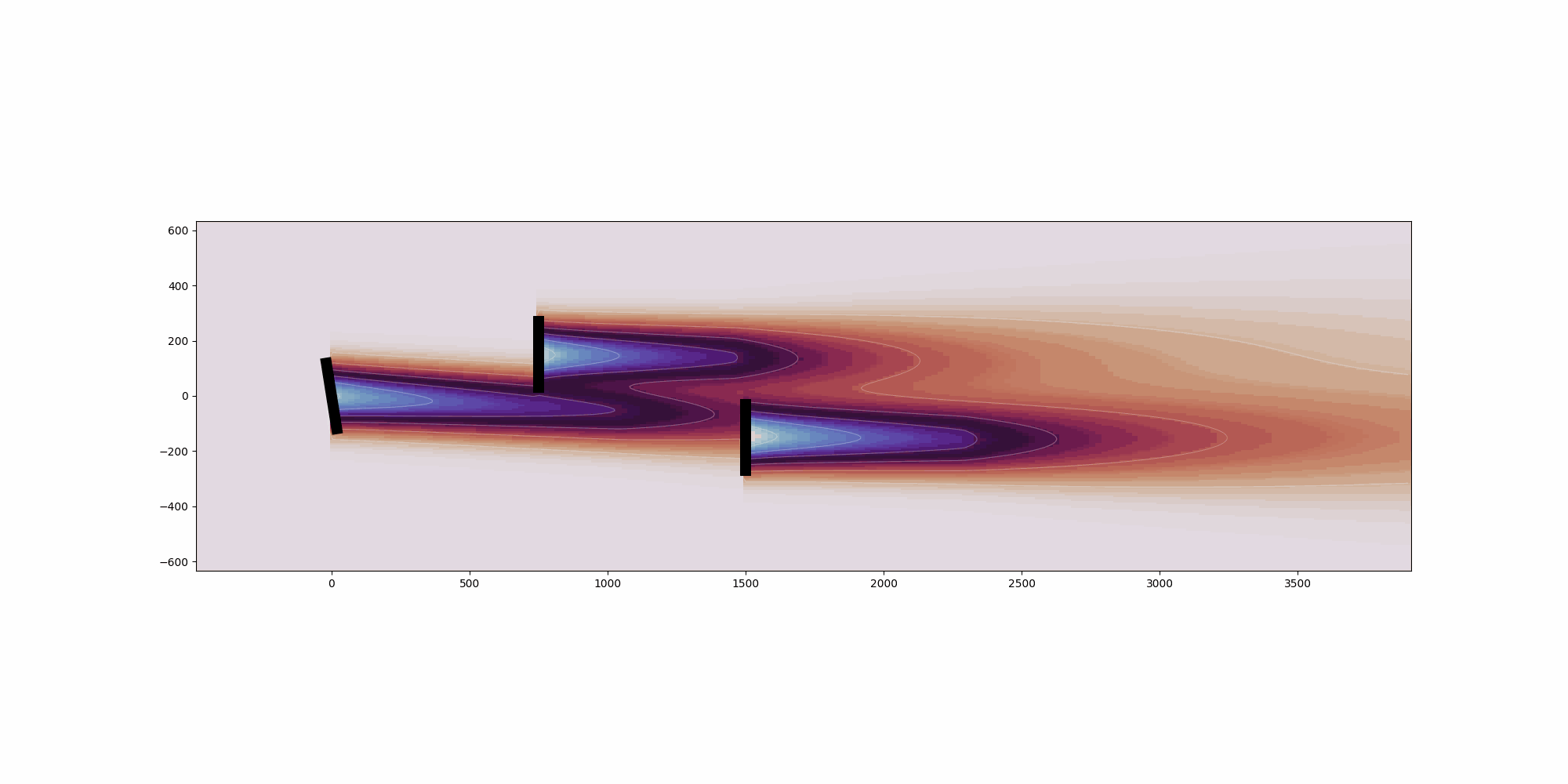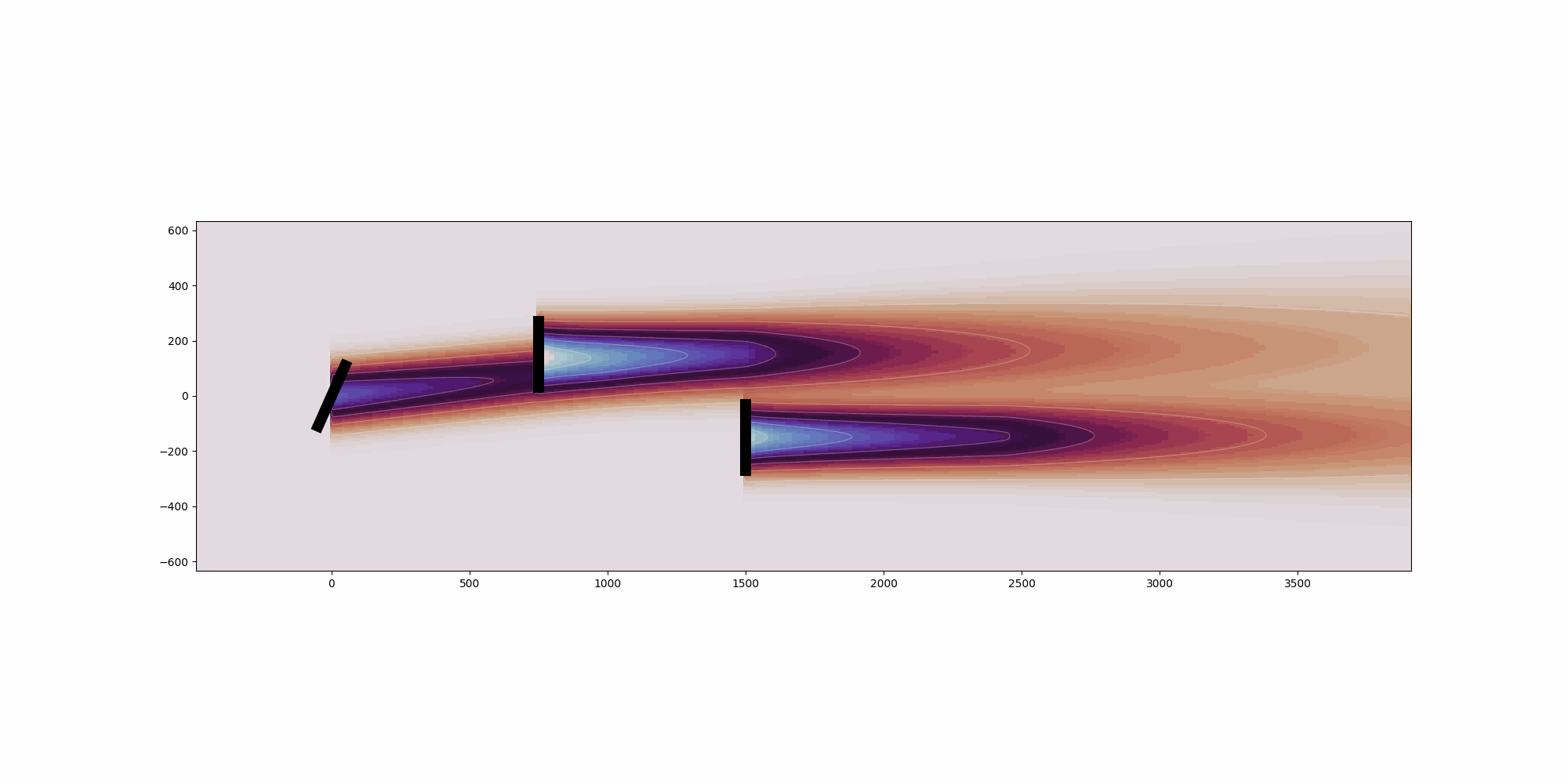
import copy
from time import perf_counter as timerpc
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from floris.logging_manager import LoggingManager
from .yaw_optimization_tools import derive_downstream_turbines
[docs]
class YawOptimization(LoggingManager):
"""
YawOptimization is a subclass of :py:class:`floris.optimization.scipy.
Optimization` that is used to optimize the yaw angles of all turbines in a Floris
Farm for a single set of inflow conditions using the SciPy optimize package.
"""
def __init__(
self,
fmodel,
minimum_yaw_angle=0.0,
maximum_yaw_angle=25.0,
yaw_angles_baseline=None,
x0=None,
turbine_weights=None,
normalize_control_variables=False,
calc_baseline_power=True,
exclude_downstream_turbines=True,
verify_convergence=False,
):
"""
Instantiate YawOptimization object with a FlorisModel object
and assign parameter values.
Args:
fmodel (:py:class:`~.floris_model.FlorisModel`): A FlorisModel object.
minimum_yaw_angle (float or ndarray): Minimum constraint on yaw
angle (deg). If a single value specified, assumes this value
for all turbines. If a 1D array is specified, assumes these
limits for each turbine specifically, but uniformly across
all atmospheric conditions. If a 2D array, limits are specific
both to the turbine and to the atmospheric condition.
Defaults to 0.0.
maximum_yaw_angle (float or ndarray): Maximum constraint on yaw
angle (deg). If a single value specified, assumes this value
for all turbines. If a 1D array is specified, assumes these
limits for each turbine specifically, but uniformly across
all atmospheric conditions. If a 2D array, limits are specific
both to the turbine and to the atmospheric condition.
Defaults to 25.0.
yaw_angles_baseline (iterable, optional): The baseline yaw
angles used to calculate the initial and baseline power
production in the wind farm and used to normalize the cost
function. If none are specified, this variable is set equal
to the current yaw angles in floris. Note that this variable
need not meet the yaw constraints specified in self.bnds,
yet a warning is raised if it does to inform the user.
Defaults to None.
x0 (iterable, optional): The initial guess for the optimization
problem. These values must meet the constraints specified
in self.bnds. Note that, if exclude_downstream_turbines=True,
the initial guess for any downstream turbines are ignored
since they are not part of the optimization. Instead, the yaw
angles for those turbines are 0.0 if that meets the lower and
upper bound, or otherwise as close to 0.0 as feasible. If no
values for x0 are specified, x0 is set to be equal to zeros
wherever feasible (w.r.t. the bounds), and equal to the
average of its lower and upper bound for all non-downstream
turbines otherwise. Defaults to None.
turbine_weights (iterable, optional): weighing terms that allow
the user to emphasize power gains at particular turbines or
completely ignore power gains from other turbines. The array
of turbine powers from floris is multiplied with this array
in the calculation of the objective function. If None, this
is an array with all values 1.0 and length equal to the
number of turbines. Defaults to None.
calc_init_power (bool, optional): If True, calculates initial
wind farm power for each set of wind conditions. Defaults to
True.
exclude_downstream_turbines (bool, optional): If True,
automatically finds and excludes turbines that are most
downstream from the optimization problem. This significantly
reduces computation time at no loss in performance. The yaw
angles of these downstream turbines are fixed to 0.0 deg if
the yaw bounds specified in self.bnds allow that, or otherwise
are fixed to the lower or upper yaw bound, whichever is closer
to 0.0. Defaults to False.
verify_convergence (bool, optional): specifies whether the found
optimal yaw angles will be checked for accurately convergence.
With large farms, especially when using SciPy or other global
optimization methods, solutions do not always converge and
turbines that should have a 0.0 deg actually have a 1.0 deg
angle, for example. By enabling this function, the final yaw
angles are compared to their baseline values one-by-one for
the turbines to make sure no such convergence issues arise.
Defaults to False.
"""
# Save turbine object to self
self.fmodel = fmodel.copy()
self.nturbs = len(self.fmodel.layout_x)
# # Check floris options
# if self.fmodel.core.flow_field.n_wind_speeds > 1:
# raise NotImplementedError(
# "Optimizer currently does not support more than one wind" +
# " speed. Please assign FLORIS a single wind speed."
# )
# Initialize optimizer
self.verify_convergence = verify_convergence
if yaw_angles_baseline is not None:
yaw_angles_baseline = self._unpack_variable(yaw_angles_baseline)
self.yaw_angles_baseline = yaw_angles_baseline
else:
b = self.fmodel.core.farm.yaw_angles
self.yaw_angles_baseline = self._unpack_variable(b)
if np.any(np.abs(b) > 0.0):
print(
"INFO: Baseline yaw angles were not specified and "
"were derived from the floris object."
)
print(
"INFO: The inherent yaw angles in the floris object "
"are not all 0.0 degrees."
)
# Set optimization bounds
self.minimum_yaw_angle = self._unpack_variable(minimum_yaw_angle)
self.maximum_yaw_angle = self._unpack_variable(maximum_yaw_angle)
# Set initial condition for optimization
if x0 is not None:
self.x0 = self._unpack_variable(x0)
else:
self.x0 = self._unpack_variable(0.0)
for ti in range(self.nturbs):
yaw_lb = self.minimum_yaw_angle[:, ti]
yaw_ub = self.maximum_yaw_angle[:, ti]
idx = (yaw_lb > 0.0) | (yaw_ub < 0.0)
self.x0[idx, ti] = (yaw_lb[idx] + yaw_ub[idx]) / 2.0
# Check inputs for consistency
if np.any(self.yaw_angles_baseline < self.minimum_yaw_angle):
print("INFO: yaw_angles_baseline exceed lower bound constraints.")
if np.any(self.yaw_angles_baseline > self.maximum_yaw_angle):
print("INFO: yaw_angles_baseline exceed upper bound constraints.")
if np.any(self.x0 < self.minimum_yaw_angle):
raise ValueError("Initial guess x0 exceeds lower bound constraints.")
if np.any(self.x0 > self.maximum_yaw_angle):
raise ValueError("Initial guess x0 exceeds upper bound constraints.")
# Define turbine weighing terms
if turbine_weights is None:
self.turbine_weights = self._unpack_variable(1.0)
else:
self.turbine_weights = self._unpack_variable(turbine_weights)
# Save remaining user options to self
self.normalize_variables = normalize_control_variables
self.calc_baseline_power = calc_baseline_power
self.exclude_downstream_turbines = exclude_downstream_turbines
# Prepare for optimization and calculate baseline powers (if applic.)
self._initialize()
self._calculate_baseline_farm_power()
# Initialize optimal yaw angles and cost function as baseline values
self._yaw_angles_opt_subset = copy.deepcopy(self._yaw_angles_baseline_subset)
self._farm_power_opt_subset = copy.deepcopy(self._farm_power_baseline_subset)
self._yaw_lbs = copy.deepcopy(self._minimum_yaw_angle_subset)
self._yaw_ubs = copy.deepcopy(self._maximum_yaw_angle_subset)
# Private methods
def _initialize(self):
# Reduce optimization problem as much as possible
self._reduce_control_problem()
# Normalize optimization variables
if self.normalize_variables:
self._normalize_control_problem()
def _unpack_variable(self, variable, subset=False):
"""Take a variable, can be either a float, a list equal in
length to the number of turbines, or an ndarray. It then
upsamples this value so that it always matches the dimensions
(self.nconds, self.nturbs).
"""
# Deal with full vs. subset dimensions
nturbs = self.nturbs
if subset:
nturbs = np.shape(self._x0_subset.shape[1])
# Then process maximum yaw angle
if isinstance(variable, (int, float)):
# If single value, copy over to all turbines
variable = np.tile(variable, (nturbs))
variable = np.array(variable, dtype=float)
if len(np.shape(variable)) == 1:
# If one-dimensional array, copy over to all atmos. conditions
variable = np.tile(
variable,
(self.fmodel.core.flow_field.n_findex, 1)
)
return variable
def _reduce_control_problem(self):
"""
This function reduces the control problem by eliminating turbines
of which the yaw angles need not be optimized, either because of a
user-specified set of bounds (where bounds[i][0] == bounds[i][1]),
or alternatively turbines that are far downstream in the wind farm
and of which the wake does not impinge other turbines, if
exclude_downstream_turbines == True.
"""
# Initialize which turbines to optimize for
self.turbs_to_opt = (self.maximum_yaw_angle - self.minimum_yaw_angle >= 0.001)
# Initialize subset variables as full set
self.fmodel_subset = self.fmodel.copy()
n_findex_subset = copy.deepcopy(self.fmodel.core.flow_field.n_findex)
minimum_yaw_angle_subset = copy.deepcopy(self.minimum_yaw_angle)
maximum_yaw_angle_subset = copy.deepcopy(self.maximum_yaw_angle)
x0_subset = copy.deepcopy(self.x0)
turbs_to_opt_subset = copy.deepcopy(self.turbs_to_opt)
turbine_weights_subset = copy.deepcopy(self.turbine_weights)
yaw_angles_template_subset = self._unpack_variable(0.0)
yaw_angles_baseline_subset = copy.deepcopy(self.yaw_angles_baseline)
# Define which turbines to optimize for
if self.exclude_downstream_turbines:
for iw, wd in enumerate(self.fmodel.core.flow_field.wind_directions):
# Remove turbines from turbs_to_opt that are downstream
downstream_turbines = derive_downstream_turbines(self.fmodel, wd)
downstream_turbines = np.array(downstream_turbines, dtype=int)
self.turbs_to_opt[iw, downstream_turbines] = False
turbs_to_opt_subset = copy.deepcopy(self.turbs_to_opt) # Update
# Set up a template yaw angles array with default solutions. The default
# solutions are either 0.0 or the allowable yaw angle closest to 0.0 deg.
# This solution addresses both downstream turbines, minimizing their abs.
# yaw offset, and additionally fixing equality-constrained turbines to
# their appropriate yaw angle.
idx = (minimum_yaw_angle_subset > 0.0) | (maximum_yaw_angle_subset < 0.0)
if np.any(idx):
# Find bounds closest to 0.0 deg
combined_bounds = np.concatenate(
(
np.expand_dims(minimum_yaw_angle_subset, axis=3),
np.expand_dims(maximum_yaw_angle_subset, axis=3)
),
axis=3
)
# Overwrite all values that are not allowed to be 0.0 with bound value closest to zero
ids_closest = np.expand_dims(np.argmin(np.abs(combined_bounds), axis=3), axis=3)
yaw_mb = np.squeeze(np.take_along_axis(combined_bounds, ids_closest, axis=3))
yaw_angles_template_subset[idx] = yaw_mb[idx]
# Save all subset variables to self
self._n_findex_subset = n_findex_subset
self._minimum_yaw_angle_subset = minimum_yaw_angle_subset
self._maximum_yaw_angle_subset = maximum_yaw_angle_subset
self._x0_subset = x0_subset
self._turbs_to_opt_subset = turbs_to_opt_subset
self._turbine_weights_subset = turbine_weights_subset
self._yaw_angles_template_subset = yaw_angles_template_subset
self._yaw_angles_baseline_subset = yaw_angles_baseline_subset
def _normalize_control_problem(self):
"""
This private function normalizes variables for the optimization
problem, specifically the initial condition x0 and the bounds.
Normalization can improve optimization performance when using common
optimization methods such as the SciPy Optimization Toolbox.
"""
lb = np.min(self._minimum_yaw_angle_subset)
ub = np.max(self._maximum_yaw_angle_subset)
self._normalization_length = (ub - lb)
self._x0_subset_norm = self._x0_subset / self._normalization_length
self._minimum_yaw_angle_subset_norm = (
self._minimum_yaw_angle_subset
/ self._normalization_length
)
self._maximum_yaw_angle_subset_norm = (
self._maximum_yaw_angle_subset
/ self._normalization_length
)
def _calculate_farm_power(
self,
yaw_angles=None,
wd_array=None,
ws_array=None,
ti_array=None,
turbine_weights=None,
heterogeneous_speed_multipliers=None,
):
"""
Calculate the wind farm power production assuming the predefined
probability distribution (self.unc_options/unc_pmf), with the
appropriate weighing terms, and for a specific set of yaw angles.
Args:
yaw_angles (iterable, optional): Array or list of yaw angles in degrees.
Defaults to None.
wd_array (iterable, optional): Array or list of wind directions in degrees.
Defaults to None.
ws_array (iterable, optional): Array or list of wind speeds in m/s. Defaults to None.
ti_array (iterable, optional): Array or list of turbulence intensities.
Defaults to None.
turbine_weights (iterable, optional): Array or list of weights to apply to the turbine
powers. Defaults to None.
heterogeneous_speed_multipliers (iterable, optional): Array or list of speed up factors
for heterogeneous inflow. Defaults to None.
Returns:
farm_power (float): Weighted wind farm power.
"""
# Unpack all variables, whichever are defined.
fmodel_subset = copy.deepcopy(self.fmodel_subset)
if wd_array is None:
wd_array = fmodel_subset.core.flow_field.wind_directions
if ws_array is None:
ws_array = fmodel_subset.core.flow_field.wind_speeds
if ti_array is None:
ti_array = fmodel_subset.core.flow_field.turbulence_intensities
if yaw_angles is None:
yaw_angles = self._yaw_angles_baseline_subset
if turbine_weights is None:
turbine_weights = self._turbine_weights_subset
if heterogeneous_speed_multipliers is not None:
fmodel_subset.core.flow_field.\
heterogeneous_inflow_config['speed_multipliers'] = heterogeneous_speed_multipliers
# Ensure format [incompatible with _subset notation]
yaw_angles = self._unpack_variable(yaw_angles, subset=True)
# # Correct wind direction definition: 270 deg is from left, cw positive
# wd_array = wrap_360(wd_array)
# Calculate solutions
turbine_power = np.zeros_like(self._minimum_yaw_angle_subset[:, :])
fmodel_subset.set(
wind_directions=wd_array,
wind_speeds=ws_array,
turbulence_intensities=ti_array,
yaw_angles=yaw_angles,
)
fmodel_subset.run()
turbine_power = fmodel_subset.get_turbine_powers()
# Multiply with turbine weighing terms
turbine_power_weighted = np.multiply(turbine_weights, turbine_power)
farm_power_weighted = np.sum(turbine_power_weighted, axis=1)
return farm_power_weighted
def _calculate_baseline_farm_power(self):
"""
Calculate the weighted wind farm power under the baseline turbine yaw
angles.
"""
if self.calc_baseline_power:
P = self._calculate_farm_power(self._yaw_angles_baseline_subset)
self._farm_power_baseline_subset = P
self.farm_power_baseline = P
else:
self._farm_power_baseline_subset = None
self.farm_power_baseline = None
def _finalize(self, farm_power_opt_subset=None, yaw_angles_opt_subset=None):
# Process final solutions
if farm_power_opt_subset is None:
farm_power_opt_subset = self._farm_power_opt_subset
if yaw_angles_opt_subset is None:
yaw_angles_opt_subset = self._yaw_angles_opt_subset
# Now verify solutions for convergence, if necessary
if self.verify_convergence:
yaw_angles_opt_subset, farm_power_opt_subset = (
self._verify_solutions_for_convergence(
farm_power_opt_subset,
yaw_angles_opt_subset
)
)
# Finalization step for optimization: undo reduction step
self.farm_power_opt = farm_power_opt_subset
self.yaw_angles_opt = yaw_angles_opt_subset
# Produce output table
df_list = []
df_list.append(
pd.DataFrame(
{
"wind_direction": self.fmodel.core.flow_field.wind_directions,
"wind_speed": self.fmodel.core.flow_field.wind_speeds,
"turbulence_intensity": self.fmodel.core.flow_field.turbulence_intensities,
"yaw_angles_opt": list(self.yaw_angles_opt[:, :]),
"farm_power_opt": None
if self.farm_power_opt is None
else self.farm_power_opt[:],
"farm_power_baseline": None
if self.farm_power_baseline is None
else self.farm_power_baseline[:],
}
)
)
df_opt = pd.concat(df_list, axis=0)
return df_opt
def _verify_solutions_for_convergence(
self,
farm_power_opt_subset,
yaw_angles_opt_subset,
min_yaw_offset=0.01,
min_power_gain_for_yaw=0.02,
verbose=True,
):
"""
This function verifies whether the found solutions (yaw_angles_opt)
have any nonzero yaw angles that are actually a result of incorrect
convergence. By evaluating the power production by setting each turbine's
yaw angle to 0.0 deg, one by one, we verify that the found
optimal values do in fact lead to a nonzero power production gain.
Args:
farm_power_opt_subset (iterable): Array with the optimal wind
farm power values (i.e., farm powers with yaw_angles_opt_subset).
yaw_angles_opt_subset (iterable): Array with the optimal yaw angles
for all turbines in the farm (or for all the to-be-optimized
turbines in the farm). The yaw angles in this array will be
verified.
min_yaw_offset (float, optional): Values that differ by less than
this amount compared to the baseline value will be assumed to be
too small to make any notable difference. Therefore, for practical
reasons, the value is overwritten by its baseline value (which
typically is 0.0 deg). Defaults to 0.01.
min_power_gain_for_yaw (float, optional): The minimum percentage
uplift a turbine must create in the farm power production for its
yaw offset to be considered non negligible. Set to 0.0 to ignore
this criteria. Defaults to 0.02 (implying 0.02%).
verbose (bool, optional): Print to console. Defaults to True.
Returns:
x_opt (iterable): Array with the optimal yaw angles, possibly
with certain values being set to 0.0 deg as they were found
to be a result of incorrect convergence. If the optimization
has perfectly converged, x_opt will be identical to the user-
provided input yaw_angles_opt.
"""
print("Verifying convergence of the found optimal yaw angles.")
# Start timer
start_time = timerpc()
# Define variables locally
yaw_angles_opt_subset = np.array(yaw_angles_opt_subset, copy=True)
yaw_angles_baseline_subset = self._yaw_angles_baseline_subset
farm_power_baseline_subset = self._farm_power_baseline_subset
turbs_to_opt_subset = self._turbs_to_opt_subset
# Round small nonzero yaw angles to zero
ydiff = np.abs(yaw_angles_opt_subset - yaw_angles_baseline_subset)
ids = np.where((ydiff < min_yaw_offset) & (ydiff > 0.0))
if len(ids[0]) > 0:
if verbose:
print(f"Rounding {len(ids)} insignificant yaw angles to their baseline value.")
yaw_angles_opt_subset[ids] = yaw_angles_baseline_subset[ids]
ydiff[ids] = 0.0
# Turbines to test whether their angles sufficiently improve farm power
ids = np.where((turbs_to_opt_subset) & (ydiff > min_yaw_offset))
# Define situations that need to be calculated and find farm power.
# Each situation basically contains the exact same conditions as the
# baseline conditions and optimal yaw angles, besides for a single
# turbine for which its yaw angle was set to its baseline value (
# typically 0.0 deg). This way, we investigate whether the yaw offset
# of that turbine really adds significant uplift to the farm power
# production.
# For each turbine in the farm, reset its values to baseline. Thus,
# we copy the atmospheric conditions n_turbs times and for each
# copy of atmospheric conditions, we reset that turbine's yaw angle
# to its baseline value for all conditions.
n_turbs = len(self.fmodel.layout_x)
sp = (n_turbs, 1) # Tile shape for matrix expansion
wd_array_nominal = self.fmodel_subset.core.flow_field.wind_directions
ws_array_nominal = self.fmodel_subset.core.flow_field.wind_speeds
ti_array_nominal = self.fmodel_subset.core.flow_field.turbulence_intensities
n_wind_directions = len(wd_array_nominal)
yaw_angles_verify = np.tile(yaw_angles_opt_subset, sp)
yaw_angles_bl_verify = np.tile(yaw_angles_baseline_subset, sp)
turbine_id_array = np.zeros(np.shape(yaw_angles_verify)[0], dtype=int)
for ti in range(n_turbs):
ids = ti * n_wind_directions + np.arange(n_wind_directions)
yaw_angles_verify[ids, ti] = yaw_angles_bl_verify[ids, ti]
turbine_id_array[ids] = ti
# Now evaluate all situations
farm_power_baseline_verify = np.tile(farm_power_baseline_subset, (n_turbs))
farm_power = self._calculate_farm_power(
yaw_angles=yaw_angles_verify,
wd_array=np.tile(wd_array_nominal, n_turbs),
ws_array=np.tile(ws_array_nominal, n_turbs),
ti_array=np.tile(ti_array_nominal, n_turbs),
turbine_weights=np.tile(self._turbs_to_opt_subset, sp)
)
# Calculate power uplift for optimal solutions
uplift_o = 100 * (
np.tile(farm_power_opt_subset, (n_turbs)) /
farm_power_baseline_verify - 1.0
)
# Calculate power uplift for all cases we evaluated
uplift_n = 100.0 * (farm_power / farm_power_baseline_verify - 1.0)
# Check difference in uplift, where each row represents a different
# situation (i.e., where one turbine was set to its baseline yaw angle
# instead of its optimal yaw angle).
dp = uplift_o - uplift_n
ids_to_simplify = np.where(dp < min_power_gain_for_yaw)
ids_to_simplify = (
np.remainder(ids_to_simplify[0], n_wind_directions), # Wind direction identifier
turbine_id_array[ids_to_simplify[0]], # Turbine identifier
)
# Overwrite yaw angles that insufficiently increased farm power with baseline values
yaw_angles_opt_subset[ids_to_simplify] = (
yaw_angles_baseline_subset[ids_to_simplify]
)
n = len(ids_to_simplify[0])
if n > 0:
# Yaw angles notably changed: recalculate farm powers
farm_power_opt_subset_new = (
self._calculate_farm_power(yaw_angles_opt_subset)
)
if verbose:
# Calculate old uplift for all conditions
dP_old = 100.0 * (
farm_power_opt_subset /
farm_power_baseline_subset
) - 100.0
# Calculate new uplift for all conditions
dP_new = 100.0 * (
farm_power_opt_subset_new /
farm_power_baseline_subset
) - 100.0
# Calculate differences in power uplift
diff_uplift = dP_old - dP_new
ids_max_loss = np.where(np.nanmax(diff_uplift) == diff_uplift)
jj = (ids_max_loss[0][0], ids_max_loss[1][0])
ws_array_nominal = self.fmodel_subset.core.flow_field.wind_speeds
print(
"Nullified the optimal yaw offset for {:d}".format(n) +
" conditions and turbines."
)
print(
"Simplifying the yaw angles for these conditions lead " +
"to a maximum change in wake-steering power uplift from "
+ "{:.5f}% to {:.5f}% at ".format(dP_old[jj], dP_new[jj])
+ " WD = {:.1f} deg and WS = {:.1f} m/s.".format(
wd_array_nominal[jj[0]], ws_array_nominal[jj[1]],
)
)
t = timerpc() - start_time
print(
"Time spent to verify the convergence of the optimal " +
"yaw angles: {:.3f} s.".format(t)
)
# Return optimal solutions to the user
farm_power_opt_subset = farm_power_opt_subset_new
return yaw_angles_opt_subset, farm_power_opt_subset
# Supporting functions
def _norm(self, val, x1, x2):
"""
Normalize a variable to a value range.
Args:
val ([float]): Value to normalize.
x1 ([float]): Normalization lower bound.
x2 ([float]): Normalization upper bound.
Returns:
val_norm: Normalized variable.
"""
return (val - x1) / (x2 - x1)
def _unnorm(self, val_norm, x1, x2):
"""
Unnormalize a variable to a value range.
Args:
val_norm ([float]): Normalized value.
x1 ([float]): Normalization lower bound.
x2 ([float]): Normalization upper bound.
Returns:
val: Unnormalized variable.
"""
return np.array(val_norm) * (x2 - x1) + x1