from __future__ import annotations
import copy
import warnings
from typing import Union
import attrs
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.colors as mplcolors
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from attrs import define, field
from matplotlib import rcParams
from scipy.spatial import ConvexHull
from floris import FlorisModel
from floris.core import Core
from floris.core.turbine.operation_models import POWER_SETPOINT_DEFAULT
from floris.cut_plane import CutPlane
from floris.heterogeneous_map import HeterogeneousMap
from floris.type_dec import (
floris_array_converter,
NDArrayFloat,
)
from floris.utilities import rotate_coordinates_rel_west, wind_delta
[docs]
def show():
"""
Display all open figures. This is a wrapper for `plt.show()`.
This function is useful if the user doesn't wish to import `matplotlib.pyplot`
"""
plt.show(
)
[docs]
def line_contour_cut_plane(
cut_plane,
ax=None,
levels=None,
colors=None,
label_contours=False,
**kwargs):
"""
Visualize a cut_plane as a line contour plot.
Args:
cut_plane (:py:class:`~.tools.cut_plane.CutPlane`):
CutPlane Object.
ax (:py:class:`matplotlib.pyplot.axes`): Figure axes. Defaults
to None.
levels (np.array, optional): Contour levels for plot.
Defaults to None.
colors (list, optional): Strings of color specification info.
Defaults to None.
label_contours (Boolean, optional): Flag to include a numerical contour labels
on the plot. Defaults to False.
**kwargs: Additional parameters to pass to `ax.contour`.
"""
if not ax:
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
rcParams["contour.negative_linestyle"] = "solid"
# Plot the cut-through
contours = ax.tricontour(
cut_plane.df.x1,
cut_plane.df.x2,
cut_plane.df.u,
levels=levels,
colors=colors,
extend="both",
**kwargs,
)
if label_contours:
ax.clabel(contours, contours.levels, inline=True, fontsize=10, colors="black")
# Make equal axis
ax.set_aspect("equal")
[docs]
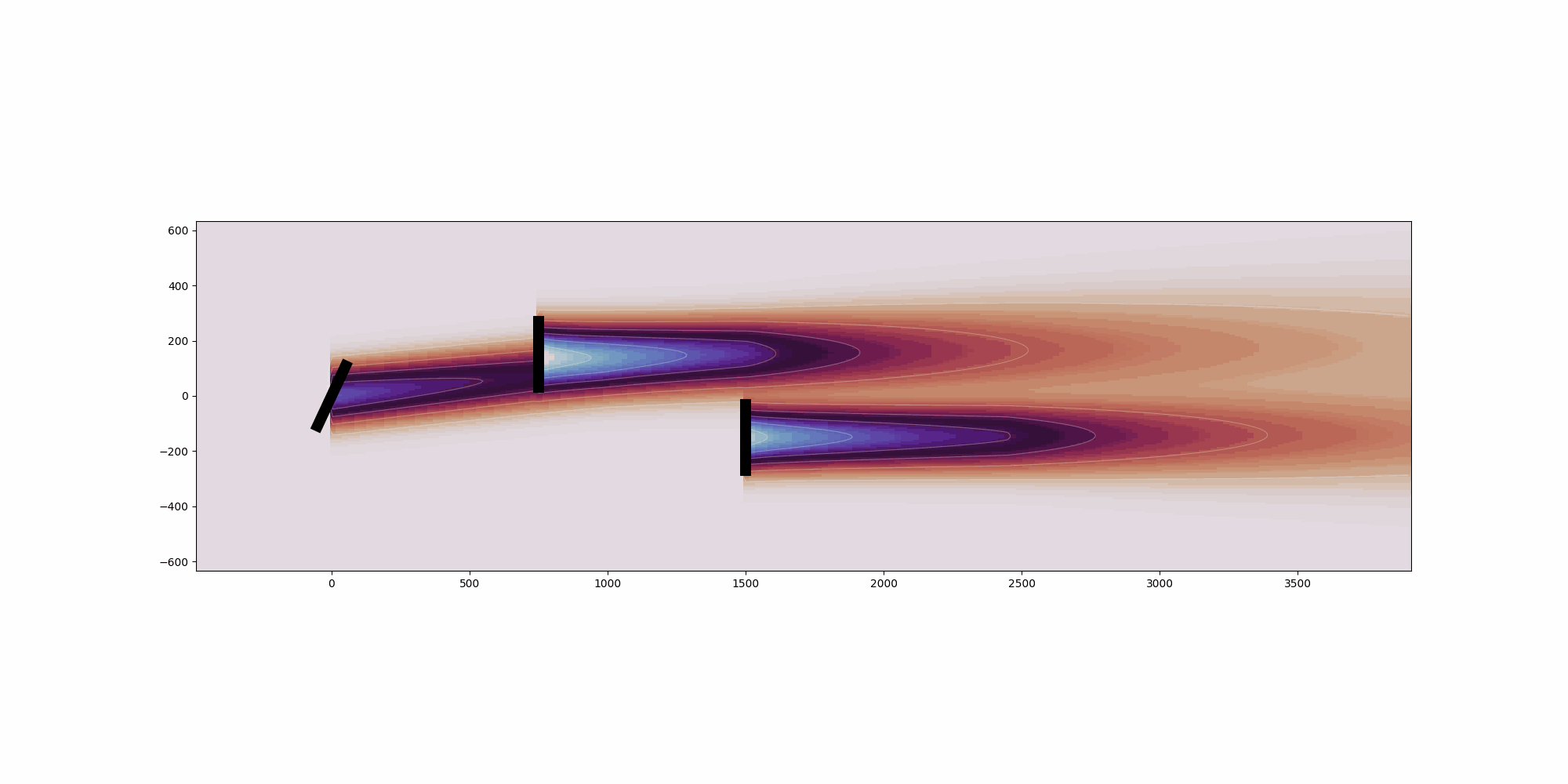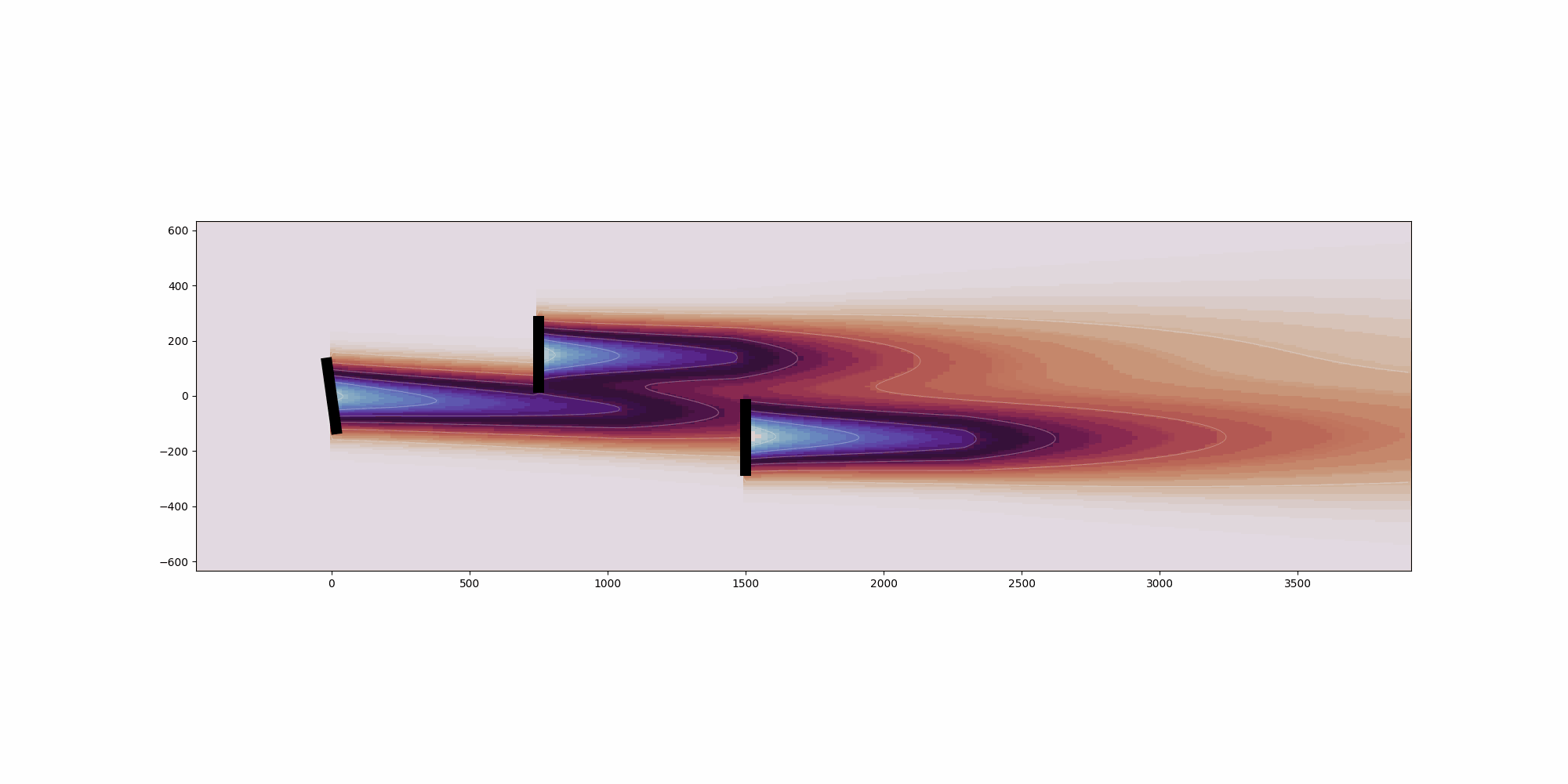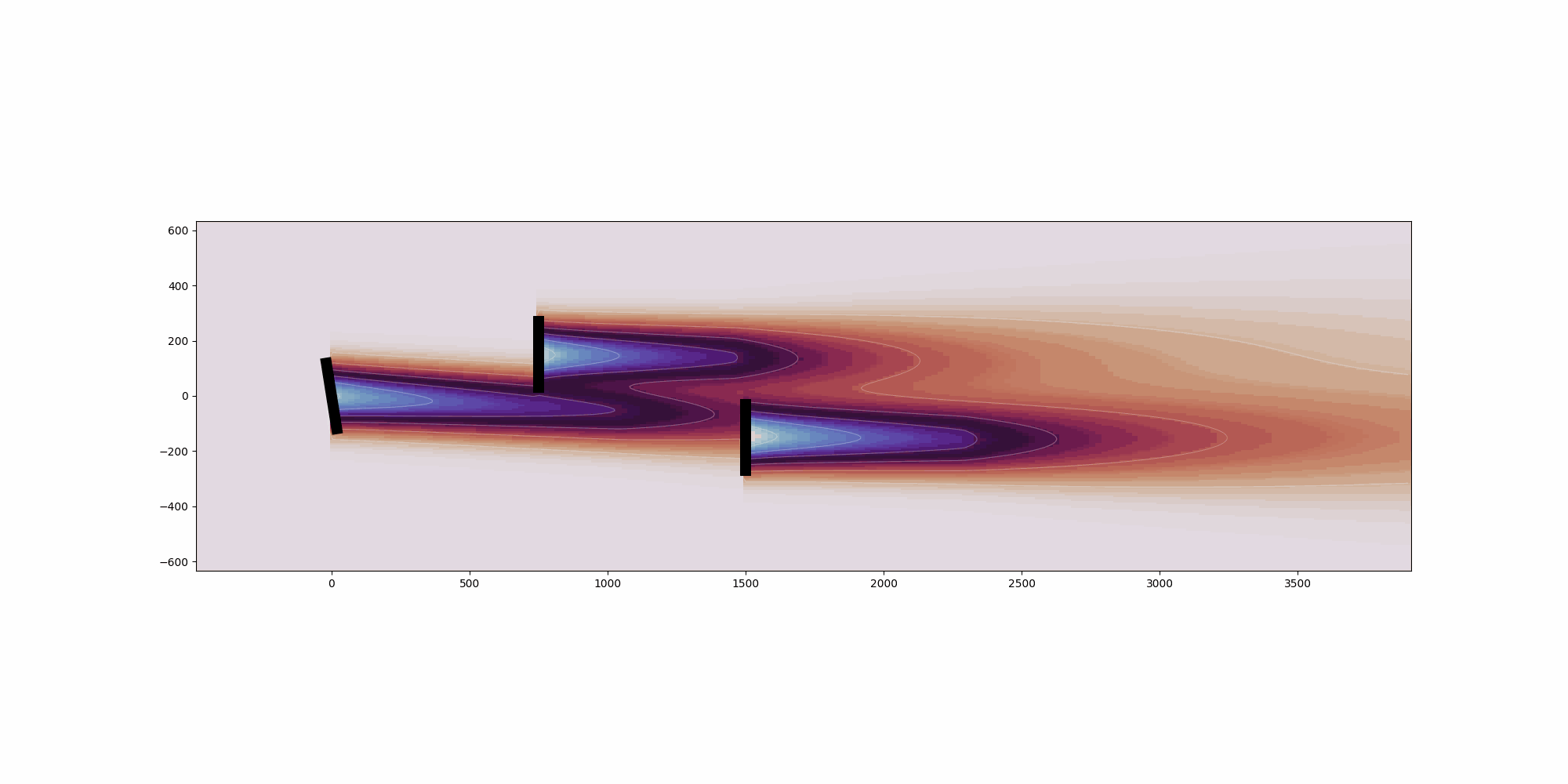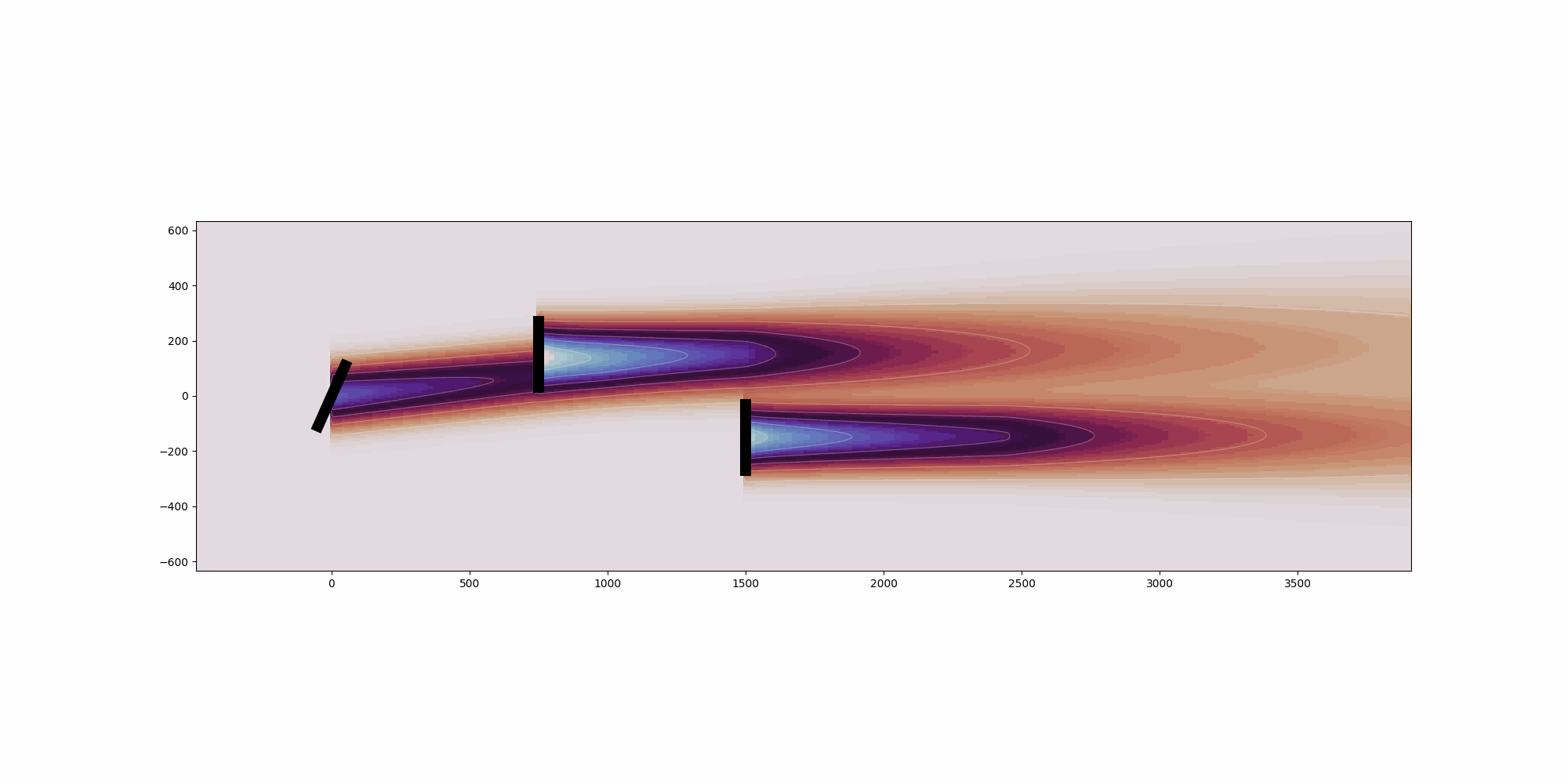
def visualize_cut_plane(
cut_plane,
ax=None,
vel_component='u',
min_speed=None,
max_speed=None,
cmap="coolwarm",
levels=None,
clevels=None,
color_bar=False,
label_contours=False,
title="",
**kwargs
):
"""
Generate pseudocolor mesh plot of the cut_plane.
Args:
cut_plane (:py:class:`~.tools.cut_plane.CutPlane`): 2D
plane through wind plant.
ax (:py:class:`matplotlib.pyplot.axes`, optional): Figure axes. Defaults
to None.
vel_component (str, optional): The velocity component that the cut plane is
perpendicular to.
min_speed (float, optional): Minimum value of wind speed for
contours. Defaults to None.
max_speed (float, optional): Maximum value of wind speed for
contours. Defaults to None.
cmap (str, optional): Colormap specifier. Defaults to
'coolwarm'.
levels (np.array, optional): Contour levels for line contour plot.
Defaults to None.
clevels (np.array, optional): Contour levels for tricontourf plot.
Defaults to None.
color_bar (Boolean, optional): Flag to include a color bar on the plot.
Defaults to False.
label_contours (Boolean, optional): Flag to include a numerical contour labels
on the plot. Defaults to False.
title (str, optional): User-supplied title for the plot. Defaults to "".
**kwargs: Additional parameters to pass to line contour plot.
Returns:
ax (:py:class:`matplotlib.pyplot.axes`): Figure axes.
"""
if not ax:
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
if vel_component=='u':
# vel_mesh = cut_plane.df.u.values.reshape(cut_plane.resolution[1], cut_plane.resolution[0])
if min_speed is None:
min_speed = cut_plane.df.u.min()
if max_speed is None:
max_speed = cut_plane.df.u.max()
elif vel_component=='v':
# vel_mesh = cut_plane.df.v.values.reshape(cut_plane.resolution[1], cut_plane.resolution[0])
if min_speed is None:
min_speed = cut_plane.df.v.min()
if max_speed is None:
max_speed = cut_plane.df.v.max()
elif vel_component=='w':
# vel_mesh = cut_plane.df.w.values.reshape(cut_plane.resolution[1], cut_plane.resolution[0])
if min_speed is None:
min_speed = cut_plane.df.w.min()
if max_speed is None:
max_speed = cut_plane.df.w.max()
# Allow separate number of levels for tricontourf and for line_contour
if clevels is None:
clevels = levels
# Plot the cut-through
im = ax.tricontourf(
cut_plane.df.x1,
cut_plane.df.x2,
cut_plane.df.u,
vmin=min_speed,
vmax=max_speed,
levels=clevels,
cmap=cmap,
extend="both",
)
# Add line contour
line_contour_cut_plane(
cut_plane,
ax=ax,
levels=levels,
colors="b",
label_contours=label_contours,
linewidths=0.8,
alpha=0.3,
**kwargs
)
if cut_plane.normal_vector == "x":
ax.invert_xaxis()
if color_bar:
cbar = plt.colorbar(im, ax=ax)
cbar.set_label('m/s')
# Set the title
ax.set_title(title)
# Make equal axis
ax.set_aspect("equal")
return ax
[docs]
def visualize_heterogeneous_cut_plane(
cut_plane,
fmodel,
ax=None,
vel_component='u',
min_speed=None,
max_speed=None,
cmap="coolwarm",
levels=None,
clevels=None,
color_bar=False,
label_contours=False,
title="",
plot_het_bounds=True,
**kwargs
):
"""
Generate pseudocolor mesh plot of the heterogeneous cut_plane.
Args:
cut_plane (:py:class:`~.tools.cut_plane.CutPlane`): 2D
plane through wind plant.
fmodel (:py:class:`~.floris_model.FlorisModel`): FlorisModel object.
ax (:py:class:`matplotlib.pyplot.axes`): Figure axes. Defaults
to None.
vel_component (str, optional): The velocity component that the cut plane is
perpendicular to.
min_speed (float, optional): Minimum value of wind speed for
contours. Defaults to None.
max_speed (float, optional): Maximum value of wind speed for
contours. Defaults to None.
cmap (str, optional): Colormap specifier. Defaults to
'coolwarm'.
levels (np.array, optional): Contour levels for line contour plot.
Defaults to None.
clevels (np.array, optional): Contour levels for tricontourf plot.
Defaults to None.
color_bar (Boolean, optional): Flag to include a color bar on the plot.
Defaults to False.
label_contours (Boolean, optional): Flag to include a numerical contour labels
on the plot. Defaults to False.
title (str, optional): User-supplied title for the plot. Defaults to "".
plot_het_bonds (boolean, optional): Flag to include the user-defined bounds of the
heterogeneous wind speed area. Defaults to True.
**kwargs: Additional parameters to pass to line contour plot.
Returns:
ax (:py:class:`matplotlib.pyplot.axes`): Figure axes.
"""
ax = visualize_cut_plane(
cut_plane=cut_plane,
ax=ax,
vel_component=vel_component,
min_speed=min_speed,
max_speed=max_speed,
cmap=cmap,
levels=levels,
clevels=clevels,
color_bar=color_bar,
label_contours=label_contours,
title=title,
**kwargs
)
if plot_het_bounds:
HeterogeneousMap.plot_heterogeneous_boundary(
fmodel.core.flow_field.heterogeneous_inflow_config['x'],
fmodel.core.flow_field.heterogeneous_inflow_config['y'],
ax=ax
)
return ax
[docs]
def visualize_quiver(cut_plane, ax=None, min_speed=None, max_speed=None, downSamp=1, **kwargs):
"""
Visualize the in-plane flows in a cut_plane using quiver.
Args:
cut_plane (:py:class:`~.tools.cut_plane.CutPlane`): 2D
plane through wind plant.
ax (:py:class:`matplotlib.pyplot.axes`): Figure axes. Defaults
to None.
min_speed (float, optional): Minimum value of wind speed for
contours. Defaults to None.
max_speed (float, optional): Maximum value of wind speed for
contours. Defaults to None.
downSamp (int, optional): Down sample the number of quiver arrows
from underlying grid.
**kwargs: Additional parameters to pass to `ax.streamplot`.
Returns:
im (:py:class:`matplotlib.plt.pcolormesh`): Image handle.
"""
if not ax:
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
# Reshape UMesh internally
x1_mesh = cut_plane.df.x1.values.reshape(cut_plane.resolution[1], cut_plane.resolution[0])
x2_mesh = cut_plane.df.x2.values.reshape(cut_plane.resolution[1], cut_plane.resolution[0])
v_mesh = cut_plane.df.v.values.reshape(cut_plane.resolution[1], cut_plane.resolution[0])
w_mesh = cut_plane.df.w.values.reshape(cut_plane.resolution[1], cut_plane.resolution[0])
# plot the stream plot
ax.streamplot(
(x1_mesh[::downSamp, ::downSamp]),
(x2_mesh[::downSamp, ::downSamp]),
v_mesh[::downSamp, ::downSamp],
w_mesh[::downSamp, ::downSamp],
# scale=80.0,
# alpha=0.75,
# **kwargs
)
# ax.quiverkey(QV1, -.75, -0.4, 1, '1 m/s', coordinates='data')
# Make equal axis
# ax.set_aspect('equal')
[docs]
def reverse_cut_plane_x_axis_in_plot(ax):
"""
Shortcut method to reverse direction of x-axis.
Args:
ax (:py:class:`matplotlib.pyplot.axes`): Figure axes.
"""
ax.invert_xaxis()
[docs]
def plot_rotor_values(
values: np.ndarray,
findex: int,
n_rows: int,
n_cols: int,
t_range: range | None = None,
cmap: str = "coolwarm",
return_fig_objects: bool = False,
save_path: Union[str, None] = None,
show: bool = False
) -> Union[None, tuple[plt.figure, plt.axes, plt.axis, plt.colorbar]]:
"""
Plots the gridded turbine rotor values. This is intended to be used for
understanding the differences between two sets of values, so each subplot can be
used for inspection of what values are differing, and under what conditions.
Parameters:
values (np.ndarray): The 4-dimensional array of values to plot. Should be:
(N findex, N turbines, N rotor points, N rotor points).
findex (int): The index for the sample point to plot.
n_rows (int): The number of rows to include for subplots. With ncols, this should
generally add up to the number of turbines in the farm.
n_cols (int): The number of columns to include for subplots. With ncols, this should
generally add up to the number of turbines in the farm.
t_range (range | None): Optional. The turbine count used to create the title for each
subplot. If not provided, the size of the 2-th dimension of `values` is used.
cmap (str): Optional. The matplotlib colormap to be used, default "coolwarm".
return_fig_objects (bool): Optional. Flag to return the primary figure objects for
further editing, default False.
save_path (str | None): Optional. Where to save the figure, if a value is provided.
show (bool): Optional. Flag to run `plt.show()` to present all the plots
currently created with matplotlib.
Returns:
None | tuple[plt.figure, plt.axes, plt.axis, plt.colorbar]: If
`return_fig_objects` is `False, then `None` is returned`, otherwise the primary
figure objects are returned for custom editing.
Example:
from floris.visualization import plot_rotor_values
plot_rotor_values(floris.flow_field.u, findex=0, n_rows=1, ncols=4)
plot_rotor_values(floris.flow_field.v, findex=0, n_rows=1, ncols=4)
plot_rotor_values(floris.flow_field.w, findex=0, n_rows=1, ncols=4, show=True)
"""
cmap = plt.cm.get_cmap(name=cmap)
if t_range is None:
t_range = range(values.shape[1])
fig = plt.figure()
axes = fig.subplots(n_rows, n_cols)
# For 1x1, fig.subplots returns an Axes object, but for more than 1x1 it returns a np.array.
# In this case, convert to an array so that the rest of this function can be simplified.
if n_rows == 1 and n_cols == 1:
axes = np.array([axes])
titles = np.array([f"tindex: {i}" for i in t_range])
for ax, t, i in zip(axes.flatten(), titles, t_range):
vmin = np.min(values[findex])
vmax = np.max(values[findex])
norm = mplcolors.Normalize(vmin, vmax)
ax.imshow(values[findex, i].T, cmap=cmap, norm=norm, origin="lower")
ax.invert_xaxis()
ax.set_xticks([])
ax.set_yticks([])
ax.set_title(t)
fig.subplots_adjust(right=0.8)
cbar_ax = fig.add_axes([0.83, 0.25, 0.03, 0.5])
cb = fig.colorbar(mpl.cm.ScalarMappable(norm=norm, cmap=cmap), cax=cbar_ax)
if save_path:
plt.savefig(save_path, bbox_inches="tight")
if return_fig_objects:
return fig, axes, cbar_ax, cb
if show:
plt.show()
[docs]
def calculate_horizontal_plane_with_turbines(
fmodel,
x_resolution=200,
y_resolution=200,
x_bounds=None,
y_bounds=None,
findex_for_viz=None,
) -> CutPlane:
"""
This function creates a :py:class:`~.tools.cut_plane.CutPlane` by
adding an additional turbine to the farm and moving it through every
a regular grid throughout the flow field. This method allows for
visualizing wake models that do not support the FullFlowGrid and
its associated solver. As the new turbine is moved around the flow
field, the velocities at its rotor are stored in local variables,
and the flow field is reset to its initial state for every new
location. Then, the local velocities are put into a DataFrame and
then into a CutPlane. This method is much slower than
`FlorisModel.calculate_horizontal_plane`, but it is helpful
for models where the visualization capability is not yet available.
Args:
fmodel (:py:class:`floris.floris_model.FlorisModel`):
Preinitialized FlorisModel object.
x_resolution (float, optional): Output array resolution. Defaults to 200 points.
y_resolution (float, optional): Output array resolution. Defaults to 200 points.
x_bounds (tuple, optional): Limits of output array (in m). Defaults to None.
y_bounds (tuple, optional): Limits of output array (in m). Defaults to None.
findex_for_viz (int, optional): Index of the condition to visualize.
Returns:
:py:class:`~.tools.cut_plane.CutPlane`: containing values of x, y, u, v, w
"""
if fmodel.core.flow_field.n_findex > 1 and findex_for_viz is None:
print(
"Multiple findices detected. Using first findex for visualization."
)
if findex_for_viz is None:
findex_for_viz = 0
# Make a local copy of fmodel to avoid editing passed in fmodel
fmodel_viz = copy.deepcopy(fmodel)
# Set the ws and wd
fmodel_viz.set_for_viz(findex_for_viz, None)
yaw_angles = fmodel_viz.core.farm.yaw_angles
power_setpoints = fmodel_viz.core.farm.power_setpoints
awc_modes = fmodel_viz.core.farm.awc_modes
awc_amplitudes = fmodel_viz.core.farm.awc_amplitudes
awc_frequencies = fmodel_viz.core.farm.awc_frequencies
# Grab the turbine layout
layout_x = copy.deepcopy(fmodel_viz.layout_x)
layout_y = copy.deepcopy(fmodel_viz.layout_y)
turbine_types = copy.deepcopy(fmodel_viz.core.farm.turbine_type)
D = fmodel_viz.core.farm.rotor_diameters_sorted[0, 0]
# Declare a new layout array with an extra turbine
layout_x_test = np.append(layout_x,[0])
layout_y_test = np.append(layout_y,[0])
# Declare turbine types with an extra turbine in case of special one-type usage
if len(layout_x) > 1 and len(turbine_types) == 1:
# Convert to list length len(layout_x) + 1
turbine_types_test = [turbine_types[0] for i in range(len(layout_x))] + ['nrel_5MW']
else:
turbine_types_test = np.append(turbine_types, 'nrel_5MW').tolist()
yaw_angles = np.append(
yaw_angles,
np.zeros([fmodel_viz.core.flow_field.n_findex, 1]),
axis=1
)
power_setpoints = np.append(
power_setpoints,
POWER_SETPOINT_DEFAULT * np.ones([fmodel_viz.core.flow_field.n_findex, 1]),
axis=1
)
awc_modes = np.append(
awc_modes,
np.full((fmodel_viz.core.flow_field.n_findex, 1), "baseline"),
axis=1
)
awc_amplitudes = np.append(
awc_amplitudes,
np.zeros([fmodel_viz.core.flow_field.n_findex, 1]),
axis=1
)
awc_frequencies = np.append(
awc_frequencies,
np.zeros([fmodel_viz.core.flow_field.n_findex, 1]),
axis=1
)
# Get a grid of points test test
if x_bounds is None:
x_bounds = (np.min(layout_x) - 2 * D, np.max(layout_x) + 10 * D)
if y_bounds is None:
y_bounds = (np.min(layout_y) - 2 * D, np.max(layout_y) + 2 * D)
# Now generate a list of points
x_points = np.linspace(x_bounds[0], x_bounds[1], x_resolution)
y_points = np.linspace(y_bounds[0], y_bounds[1], y_resolution)
num_points = len(x_points) * len(y_points)
# Now loop over the points
x_results = np.zeros(num_points)
y_results = np.zeros(num_points)
z_results = np.zeros(num_points)
u_results = np.zeros(num_points)
v_results = np.zeros(num_points)
w_results = np.zeros(num_points)
idx = 0
for y in y_points:
for x in x_points:
# Save the x and y results
x_results[idx] = x
y_results[idx] = y
# Place the test turbine at this location and calculate wake
layout_x_test[-1] = x
layout_y_test[-1] = y
fmodel_viz.set(
layout_x=layout_x_test,
layout_y=layout_y_test,
yaw_angles=yaw_angles,
power_setpoints=power_setpoints,
awc_modes=awc_modes,
awc_amplitudes=awc_amplitudes,
awc_frequencies=awc_frequencies,
turbine_type=turbine_types_test
)
fmodel_viz.run()
# Get the velocity of that test turbines central point
center_point = int(np.floor(fmodel_viz.core.flow_field.u[0,-1].shape[0] / 2.0))
u_results[idx] = fmodel_viz.core.flow_field.u[0,-1,center_point,center_point]
# Increment index
idx = idx + 1
# Make a dataframe
df = pd.DataFrame({
'x1':x_results,
'x2':y_results,
'x3':z_results,
'u':u_results,
'v':v_results,
'w':w_results,
})
# Convert to a cut_plane
horizontal_plane = CutPlane(df, x_resolution, y_resolution, "z")
return horizontal_plane