VASP
The Vienna Ab initio Simulation Package (VASP) is an application for atomic scale materials modelling from first principles. VASP computes an approximate solution to the many-body Schrödinger equation, either within density functional theory or within the Hartree-Fock approximation using pseudopotentials and plane wave basis sets. VASP can carry out a range of electronic structure and quantum-mechanical molecular dynamics calculations and has many features including hybrid functionals, Green's functions methods (GW quasiparticles, and ACFDT-RPA) and many-body perturbation theory (2nd-order Møller-Plesset). For a full list of capabilities, please see the About VASP page and for further details, documentation, forums, and FAQs, visit the VASP website.
Accessing VASP on NREL's HPC Clusters
Important
The VASP license requires users to be a member of a "workgroup" defined by the University of Vienna or Materials Design. If you are receiving "Permission denied" errors when trying to use VASP, you must be made part of the "vasp" Linux group first. To join, please contact HPC Help with the following information:
- Your name
- The workgroup PI
- Whether you are licensed through Vienna (academic) or Materials Design, Inc. (commercial)
- If licensed through Vienna:
- The e-mail address under which you are registered with Vienna as a workgroup member (this may not be the e-mail address you used to get an HPC account)
- Your VASP license ID
- If licensed through Materials Design:
- Proof of current licensed status
Once status can be confirmed, we can provide access to our VASP builds.
Getting Started
VASP is available through modules on all HPC systems. Use the command module avail vasp to view the versions of VASP available on each cluster, and module load vasp/<version> to load a specific version. If no version is specified, the default module (marked with "(D)") will be loaded. In the following sections, we will give sample input scripts and recommendations for the different builds. To run VASP, the following 4 input files are needed: POSCAR, POTCAR, INCAR, KPOINTS. For more information about VASP input files, see the VASP wiki.
Attention
If you would like to build your own VASP on Kestrel, please read our section Building VASP on Kestrel carefully before compiling on Kestrel's cray architecture.
Supported Versions
NREL offers modules for VASP 5 and VASP 6 on CPUs as well as GPUs on certain systems. See table below for current availability, as well as system specific documentation for more details on running different builds.
|
Kestrel |
Eagle |
Swift |
Vermilion |
| VASP 5 |
X |
X |
|
X |
| VASP 6 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
| VASP 6 GPU |
|
X |
|
X |
Each VASP module provides three executables where the correct one should be chosen for the type of job:
-
vasp_std is for general k-point meshes with collinear spins
-
vasp_ncl is for general k-point meshes with non-collinear spins
-
vasp_gam is for Gamma-point-only calculations
NREL also offers support for additional functionalities such as transition state theory tools from University of Texas-Austin, implicit solvation models from the University of Florida, and BEEF-vdw functionals. Please contact HPC-Help if a functionality you need is not present in one of our builds.
VASP on Kestrel
CPU
There are modules for CPU builds of VASP 5 and VASP 6 each with solvation, transition state tools, and BEEF-vdW functionals. These modules can be loaded with module load vasp/<version>.
Important: Conserving your AUs on Kestrel
Kestrel nodes have nearly 3x as many cores as Eagle. Our testing has indicated VASP DFT jobs up to 200 atoms run more efficiently on a fraction of a node (see performance notes below). We therefore highly recommend that VASP DFT users check the efficiency of their calculations and consider using the shared partition to get the most out of their allocations. Please see the sample shared job script provided below and the Shared partition documentation.
Sample job script: Kestrel - Full node
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --nodes=2
#SBATCH --tasks-per-node=104
#SBATCH --time=2:00:00
#SBATCH --account=<your-account-name>
#SBATCH --job-name=<your-job-name>
module load vasp/<version>
srun vasp_std |& tee out
Sample job script: Kestrel - Shared (partial) node
As described in detail in the Shared partition documentation, when you run on part of a node, you will be charged for the greater of either the fraction of cores (104 total) or of memory (240 GB total) requested. The script below shows how to request 1/4 of a node, but you can freely set --tasks and --mem-per-cpu as you see fit.
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --nodes=1
#SBATCH --partition=shared
#SBATCH --tasks=26 #How many cpus you want
#SBATCH --mem-per-cpu=2G #Default is 1 GB/core but 2 GB/core is a good starting place
#SBATCH --time=2:00:00
#SBATCH --account=<your-account-name>
#SBATCH --job-name=<your-job-name>
module load vasp/<version>
srun vasp_std |& tee out
Performance Notes
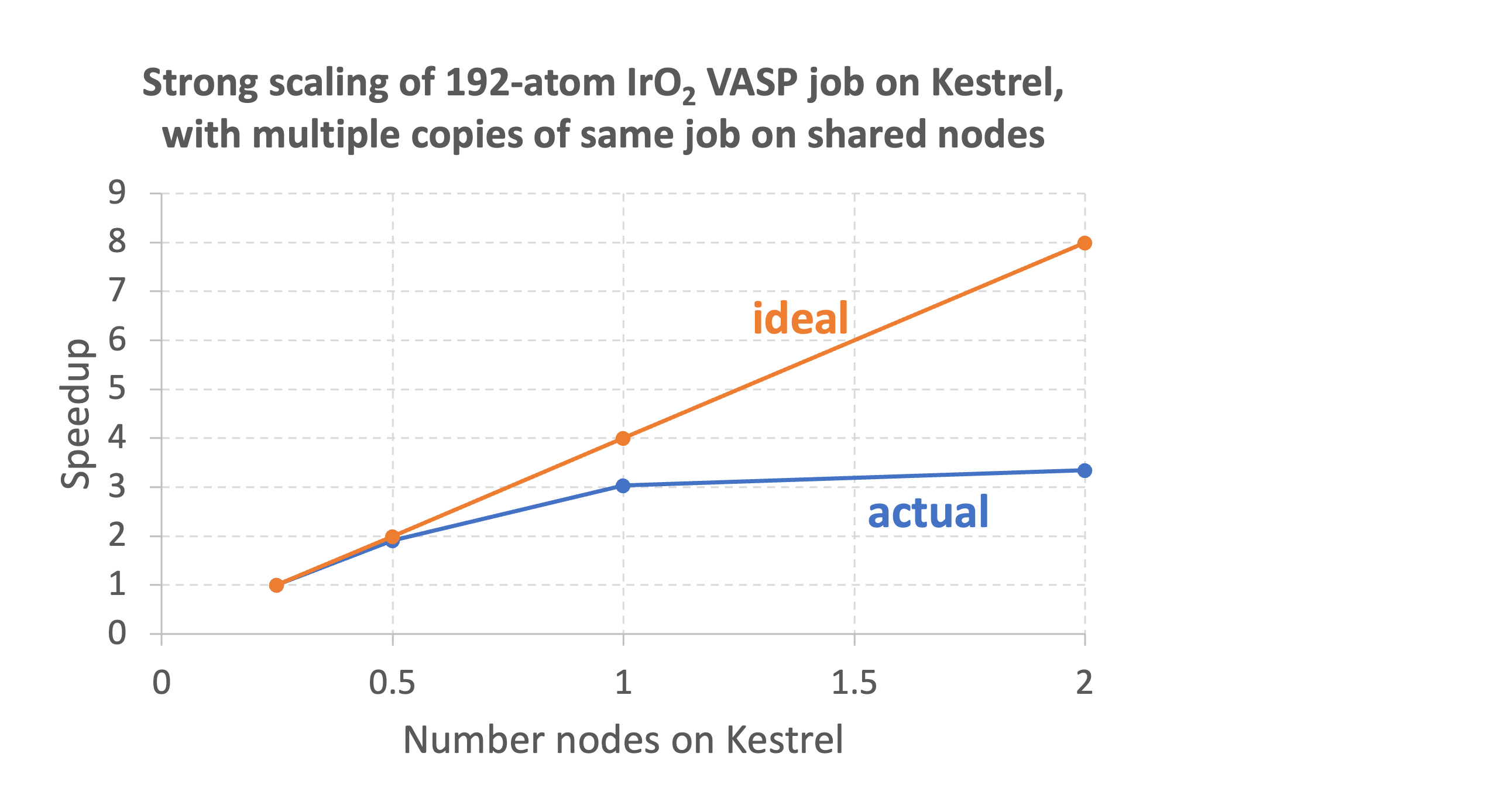
Internal testing at NREL has indicated that standard VASP DFT calculations from sizes 50-200 atoms run most efficiently on a quarter to a half node. The graph below shows the performance of a 192-atom VASP DFT job using partial nodes on the shared partition. Up to 1/2 a node, near perfect scaling is observed, but using the full node gives a speedup of only 1.5 relative to using 1/2 a node. So, the calculation will cost 50% more AUs if run on a single node compared to a half node. For a 48-atom surface Pt calculation, using the full node gives no speedup relative to using 1/2 a node, so the calculation will cost 100% more AUs if run on a single node compared to half a node.
Building VASP on Kestrel
Compiling your build
Important
On Kestrel, any modules you have loaded on the login node will be copied to a compute node, and there are many loaded by default for the cray programming environment. Make sure you are using what you intend to. Please see the Kestrel Environments for more details on programming environments.
Build recommendations for VASP
We recommend building vasp with a full intel toolchain and launching with the cray-mpich-abi at runtime. Additionally, you should build on a compute node so that you have the same architecture as at runtime:
salloc -N 1 -t <time> -A <account>
module purge
module load craype-x86-spr #specifies sapphire rapids architecture
module load intel-oneapi-compilers
module load intel-oneapi-mpi
module load intel-oneapi-mkl
Sample makefiles for vasp5 and vasp6 on Kestrel can be found in our Kestrel Repo under the vasp folder.
Running your build
Important
We have found that it is optimal to run an Intel toolchain build of VASP using cray-mpich-abi at runtime. Cray-mpich-abi has several dependencies on cray network modules, so the easiest way to load it is to first load PrgEnv-intel and then swap the default cray-mpich module for the cray-mpich-abi module swap cray-mpich cray-mpich-abi. You must then load your intel compilers and math libraries, and unload cray's libsci. A sample script showing all of this is in the dropdown below.
Sample job script: How to run your own build
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --nodes=2
#SBATCH --tasks-per-node=104
#SBATCH --time=2:00:00
#SBATCH --account=<your-account-name>
#SBATCH --job-name=<your-job-name>
# Load cray-mpich-abi and its dependencies within PrgEnv-intel, intel compilers, mkl, and unload cray's libsci
module purge
module load PrgEnv-intel
module load craype-x86-spr
module swap cray-mpich cray-mpich-abi
module unload cray-libsci
module load intel-oneapi-compilers
module load intel-oneapi-mkl
export VASP_PATH=/PATH/TO/YOUR/vasp_exe
srun ${VASP_PATH}/vasp_std |& tee out
VASP on Eagle
CPU
Sample job script: Eagle - VASP CPU
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --nodes=1
#SBATCH --time=4:00:00
#SBATCH --account=<your-account-name>
#SBATCH --job-name=<your-job-name>
module purge
#Load module
ml vasp/<version>
srun -n 36 vasp_std &> out
Performance Notes
The Intel MPI builds are recommended over the Open MPI builds as they exhibit fastest performance.
If using the openmpi builds, you may see the following warning in the vasp output that can be ignored:
Note: The following floating-point exceptions are signalling: IEEE_UNDERFLOW_FLAG IEEE_DENORMAL
Note: The following floating-point exceptions are signalling: IEEE_UNDERFLOW_FLAG
GPU
Sample job script: Eagle - VASP 6 GPU (OpenACC)
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --job-name=vasp_gpu
#SBATCH --time=1:00:00
#SBATCH --error=std.err
#SBATCH --output=std.out
#SBATCH --nodes=1
#SBATCH --gpus-per-node=2
#SBATCH --gpu-bind=map_gpu:0,1
#SBATCH --account=myaccount
#To run on multiple nodes, change the last two SBATCH lines:
##SBATCH --nodes=4
##SBATCH --gpu-bind=map_gpu:0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1 #one set of "0,1" per node
module purge
#Load the OpenACC build of VASP
ml vasp/6.3.1-nvhpc_acc
#Load some additional modules
module use /nopt/nrel/apps/220511a/modules/lmod/linux-centos7-x86_64/gcc/12.1.0
ml fftw nvhpc
mpirun -npernode 2 vasp_std &> out
Warning: ieee_invalid is signaling
Warning: ieee_divide_by_zero is signaling
Warning: ieee_underflow is signaling
Warning: ieee_inexact is signaling
FORTRAN STOP
Sample job script: Eagle - VASP 6 GPU (Cuda)
To run the Cuda build of VASP on Eagle's GPUs, we can call the vasp_gpu executable in a module for a build of VASP older than 6.3.0. To use both GPUs per node, make sure to set #SBATCH --gpus-per-node=2 and #SBATCH --ntasks-per-node=2.
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --job-name="benchmark"
#SBATCH --account=myaccount
#SBATCH --time=4:00:00
#SBATCH --nodes=1
#SBATCH --gpus-per-node=2
#SBATCH --ntasks-per-node=2
module purge
#Load Intel MPI VASP build
ml vasp/6.1.2
srun -n 2 vasp_gpu &> out
Performance Notes
The OpenACC build shows significant performance improvement compared to the Cuda build, but is more susceptible to running out of memory. The OpenACC GPU-port of VASP was released with VASP 6.2.0, and the Cuda GPU-port of VASP was dropped in VASP 6.3.0.
VASP on Swift
CPU
Sample job script: Swift - VASP 6 CPU (Intel MPI)
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --job-name="benchmark"
#SBATCH --account=myaccount
#SBATCH --time=4:00:00
#SBATCH --ntasks-per-node=64
#SBATCH --nodes=1
#Set --exclusive if you would like to prevent any other jobs from running on the same nodes (including your own)
#You will be charged for the full node regardless of the fraction of CPUs/node used
#SBATCH --exclusive
module purge
#Load Intel MPI VASP build and necessary modules
ml vaspintel
ml slurm/21-08-1-1-o2xw5ti
ml gcc/9.4.0-v7mri5d
ml intel-oneapi-compilers/2021.3.0-piz2usr
ml intel-oneapi-mpi/2021.3.0-hcp2lkf
ml intel-oneapi-mkl/2021.3.0-giz47h4
srun -n 64 vasp_std &> out
Sample job script: Swift - VASP 6 CPU (Open MPI)
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --job-name="benchmark"
#SBATCH --account=myaccount
#SBATCH --time=4:00:00
#SBATCH --ntasks-per-node=64
#SBATCH --nodes=1
#Set --exclusive if you would like to prevent any other jobs from running on the same nodes (including your own)
#You will be charged for the full node regardless of the fraction of CPUs/node used
#SBATCH --exclusive
module purge
#Load OpenMPI VASP build and necessary modules
ml vasp
ml slurm/21-08-1-1-o2xw5ti
ml openmpi/4.1.1-6vr2flz
srun -n 64 vasp_std &> out
Sample job script: Swift - run multiple jobs on the same node(s)
The following script launches two instances of srun vasp_std on the same node using an array job. Each job will be constricted to 32 cores on the node.
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --job-name="benchmark"
#SBATCH --account=myaccount
#SBATCH --time=4:00:00
#SBATCH --ntasks-per-node=32
#SBATCH --nodes=1
#Set --exclusive=user if you would like to prevent anyone else from running on the same nodes as you
#You will be charged for the full node regardless of the fraction of CPUs/node used
#SBATCH --exclusive=user
#Set how many jobs you would like to run at the same time as an array job
#In this example, an array of 2 jobs will be run at the same time. This script will be run once for each job.
#SBATCH --array=1-2
#The SLURM_ARRAY_TASK_ID variable can be used to modify the parameters of the distinct jobs in the array.
#In the case of array=1-2, the first job will have SLURM_ARRAY_TASK_ID=1, and the second will have SLURM_ARRAY_TASK_ID=2.
#For example, you could assign different input files to runs 1 and 2 by storing them in directories input_1 and input_2 and using the following code:
mkdir run_${SLURM_ARRAY_TASK_ID}
cd run_${SLURM_ARRAY_TASK_ID}
cp ../input_${SLURM_ARRAY_TASK_ID}/POSCAR .
cp ../input_${SLURM_ARRAY_TASK_ID}/POTCAR .
cp ../input_${SLURM_ARRAY_TASK_ID}/INCAR .
cp ../input_${SLURM_ARRAY_TASK_ID}/KPOINTS .
#Now load vasp and run the job...
module purge
#Load Intel MPI VASP build and necessary modules
ml vaspintel
ml slurm/21-08-1-1-o2xw5ti
ml gcc/9.4.0-v7mri5d
ml intel-oneapi-compilers/2021.3.0-piz2usr
ml intel-oneapi-mpi/2021.3.0-hcp2lkf
ml intel-oneapi-mkl/2021.3.0-giz47h4
srun -n 32 vasp_std &> out
Sample job script: Swift - run a single job on a node shared with other users
The following script launches srun vasp_std on only 32 cores on a single node. The other 32 cores remain open for other users to use. You will only be charged for half of the node hours.
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --job-name="benchmark"
#SBATCH --account=myaccount
#SBATCH --time=4:00:00
#SBATCH --ntasks-per-node=32
#SBATCH --nodes=1
#To make sure that you are only being charged for the CPUs your job is using, set mem=2GB*CPUs/node
#--mem sets the memory used per node
#SBATCH --mem=64G
module purge
#Load Intel MPI VASP build and necessary modules
ml vaspintel
ml slurm/21-08-1-1-o2xw5ti
ml gcc/9.4.0-v7mri5d
ml intel-oneapi-compilers/2021.3.0-piz2usr
ml intel-oneapi-mpi/2021.3.0-hcp2lkf
ml intel-oneapi-mkl/2021.3.0-giz47h4
srun -n 32 vasp_std &> out
Performance Notes
The Intel MPI builds are recommended over the Open MPI builds as they exhibit fastest performance.
Use at most 64 cores/node. On Swift, each node has 64 physical cores, and each core is subdivided into two virtual cores in a process that is identical to hyperthreading. Because of this, up to 128 cores can be requested from a single Swift node, but each core will only represent half of a physical core.
On Swift, VASP is most efficiently run on partially full nodes.
Unlike on Eagle, multiple jobs can run on the same nodes on Swift. If you are only using a fraction of a node, other users' jobs could be assigned to the rest of the node, which might deteriorate the performance. Setting "#SBATCH --exclusive" in your run script prevents other users from using the same node as you, but you will be charged the full 5AUs/node, regardless of the number of CPUs/node you are using.
GPU
Sample job script: Swift - VASP 6 GPU (OpenACC)
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --nodes=1
#SBATCH --partition=gpu
#SBATCH --gres=gpu:4
#SBATCH --gpu-bind=map_gpu:0,1,2,3
#SBATCH --exclusive
#SBATCH --time=1:00:00
#SBATCH --account=<your-account-name>
#SBATCH --job-name=<your-job-name>
#Load environment and openACC VASP module:
module purge
. /nopt/nrel/apps/env.sh
module use /nopt/nrel/apps/modules
module load vasp/openacc
# Note: environment will soon become default and the module will be able to be loaded with
# module purge
# module load vasp/openacc
#Launch vasp using mpirun
mpirun -npernode 4 vasp_std &> out
VASP on Vermilion
CPU
Sample job script: Vermilion - VASP 6 CPU (Intel MPI)
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --job-name=vasp
#SBATCH --nodes=1
#SBATCH --time=8:00:00
#SBATCH --error=std.err
#SBATCH --output=std.out
#SBATCH --partition=lg
#SBATCH --exclusive
#SBATCH --account=myaccount
module purge
ml vasp/6.3.1
source /nopt/nrel/apps/220525b/myenv.2110041605
ml intel-oneapi-compilers/2022.1.0-k4dysra
ml intel-oneapi-mkl/2022.1.0-akthm3n
ml intel-oneapi-mpi/2021.6.0-ghyk7n2
# some extra lines that have been shown to improve VASP reliability on Vermilion
ulimit -s unlimited
export UCX_TLS=tcp,self
export OMP_NUM_THREADS=1
ml ucx
srun --mpi=pmi2 -n 60 vasp_std
# If the multi-node calculations are breaking, replace the srun line with this line
# I_MPI_OFI_PROVIDER=tcp mpirun -iface ens7 -np 60 vasp_std
Sample job script: Vermilion - VASP 6 CPU (Open MPI)
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --job-name=vasp
#SBATCH --nodes=1
#SBATCH --time=8:00:00
#SBATCH --error=std.err
#SBATCH --output=std.out
#SBATCH --partition=lg
#SBATCH --exclusive
#SBATCH --account=myaccount
module purge
ml gcc
ml vasp/6.1.1-openmpi
# some extra lines that have been shown to improve VASP reliability on Vermilion
ulimit -s unlimited
export UCX_TLS=tcp,self
export OMP_NUM_THREADS=1
ml ucx
# lines to set "ens7" as the interconnect network
module use /nopt/nrel/apps/220525b/level01/modules/lmod/linux-rocky8-x86_64/gcc/12.1.0
module load openmpi
OMPI_MCA_param="btl_tcp_if_include ens7"
srun --mpi=pmi2 -n 60 vasp_std
Sample job script: Vermilion - VASP 5 CPU (Intel MPI)
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --job-name=vasp
#SBATCH --nodes=1
#SBATCH --time=8:00:00
##SBATCH --error=std.err
##SBATCH --output=std.out
#SBATCH --partition=lg
#SBATCH --exclusive
#SBATCH --account=myaccount
module purge
ml vasp/5.4.4
source /nopt/nrel/apps/220525b/myenv.2110041605
ml intel-oneapi-compilers/2022.1.0-k4dysra
ml intel-oneapi-mkl/2022.1.0-akthm3n
ml intel-oneapi-mpi/2021.6.0-ghyk7n2
# some extra lines that have been shown to improve VASP reliability on Vermilion
ulimit -s unlimited
export UCX_TLS=tcp,self
export OMP_NUM_THREADS=1
ml ucx
srun --mpi=pmi2 -n 60 vasp_std
# If the multi-node calculations are breaking, replace the srun line with this line
# I_MPI_OFI_PROVIDER=tcp mpirun -iface ens7 -np 60 vasp_std
Performance Notes
On Vermilion, VASP runs more performantly on a single node. Many issues have been reported for running VASP on multiple nodes, especially when requesting all available cores on each node. In order for MPI to work reliably on Vermilion, it is necessary to specify the interconnect network that Vermilion should use to communicate between nodes. If many cores are needed for your VASP calculation, it is recommended to run VASP on a singe node in the lg partition (60 cores/node), which provides the largest numbers of cores per node and use the following settings that have been shown to work well for multi-node jobs on 2 nodes. The Open MPI multi-node jobs are more reliable on Vermilion, but Intel MPI VASP jobs show better runtime performance as usual.
If your multi-node Intel MPI VASP job is crashing on Vermilion, try replacing your srun line with the following mpirun run line. -iface ens7 sets ens7 as the interconnect.
I_MPI_OFI_PROVIDER=tcp mpirun -iface ens7 -np 16 vasp_std
If your multi-node Open MPI VASP job is crashing on Vermilion, replace a call to load an openmpi module with the following lines. The OMPI_MCA_param variable sets ens7 as the interconnect.
module use /nopt/nrel/apps/220525b/level01/modules/lmod/linux-rocky8-x86_64/gcc/12.1.0
module load openmpi
OMPI_MCA_param="btl_tcp_if_include ens7"
GPU
Sample job script: Vermilion - VASP 6 CPU (OpenACC)
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --job-name=vasp
#SBATCH --nodes=2
#SBATCH --time=1:00:00
##SBATCH --error=std.err
##SBATCH --output=std.out
#SBATCH --partition=gpu
#SBATCH --gpu-bind=map_gpu:0,1,0,1
#SBATCH --exclusive
#SBATCH --account=myaccount
# Load the OpenACC build of VASP
ml vasp/6.3.1-nvhpc_acc
# Load some additional modules
module use /nopt/nrel/apps/220421a/modules/lmod/linux-rocky8-x86_64/gcc/11.3.0/
ml nvhpc
ml fftw
mpirun -npernode 1 vasp_std > vasp.$SLURM_JOB_ID
Performance Notes
The OpenACC build shows significant performance improvement compared to the Cuda build, but is more susceptible to running out of memory. The OpenACC GPU-port of VASP was released with VASP 6.2.0, and the Cuda GPU-port of VASP was dropped in VASP 6.3.0.