reV.losses.power_curve.LinearStretching
- class LinearStretching(power_curve)[source]
Bases:
AbstractPowerCurveTransformationUtility for applying a linear stretch to the power curve.
The mathematical representation of this transformation is:
\[P_{transformed}(u) = P_{original}(u/t),\]where \(P_{transformed}\) is the transformed power curve, \(P_{original}\) is the original power curve, \(u\) is the wind speed, and \(t\) is the transformation variable (wind speed multiplier).
The losses in this type of transformation are distributed primarily across regions 2 and 3 of the power curve. In particular, losses are smaller for wind speeds closer to the cut-in speed, and larger for speeds close to rated power:
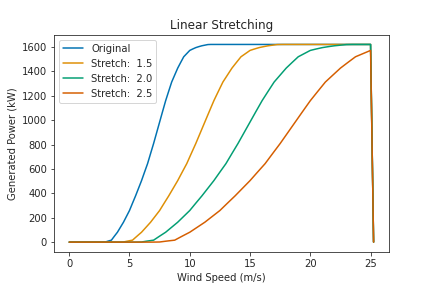
- power_curve
The “original” input power curve.
- Type:
Abstract Power Curve Transformation class.
- Parameters:
power_curve (
PowerCurve) – The turbine power curve. This input is treated as the “original” power curve.
Methods
apply(transformation_var)Apply a linear stretch to the original power curve.
Attributes
true Bounds on the wind speed multiplier (different from the optimization boundaries)
Bounds for scipy optimization, sometimes more generous than the actual fit parameter bounds which are enforced after the optimization.
- apply(transformation_var)[source]
Apply a linear stretch to the original power curve.
This function stretches the original power curve along the “wind speed” (x) axis. Any power above the cutoff speed (if one was detected) is truncated after the transformation.
- Parameters:
transformation_var (float) – The linear multiplier of the wind speed scaling.
- Returns:
PowerCurve– An new power curve containing the generation values from the shifted power curve.
- property bounds
true Bounds on the wind speed multiplier (different from the optimization boundaries)
- Type:
- property optm_bounds
Bounds for scipy optimization, sometimes more generous than the actual fit parameter bounds which are enforced after the optimization.