README Contents
ALTRIOS

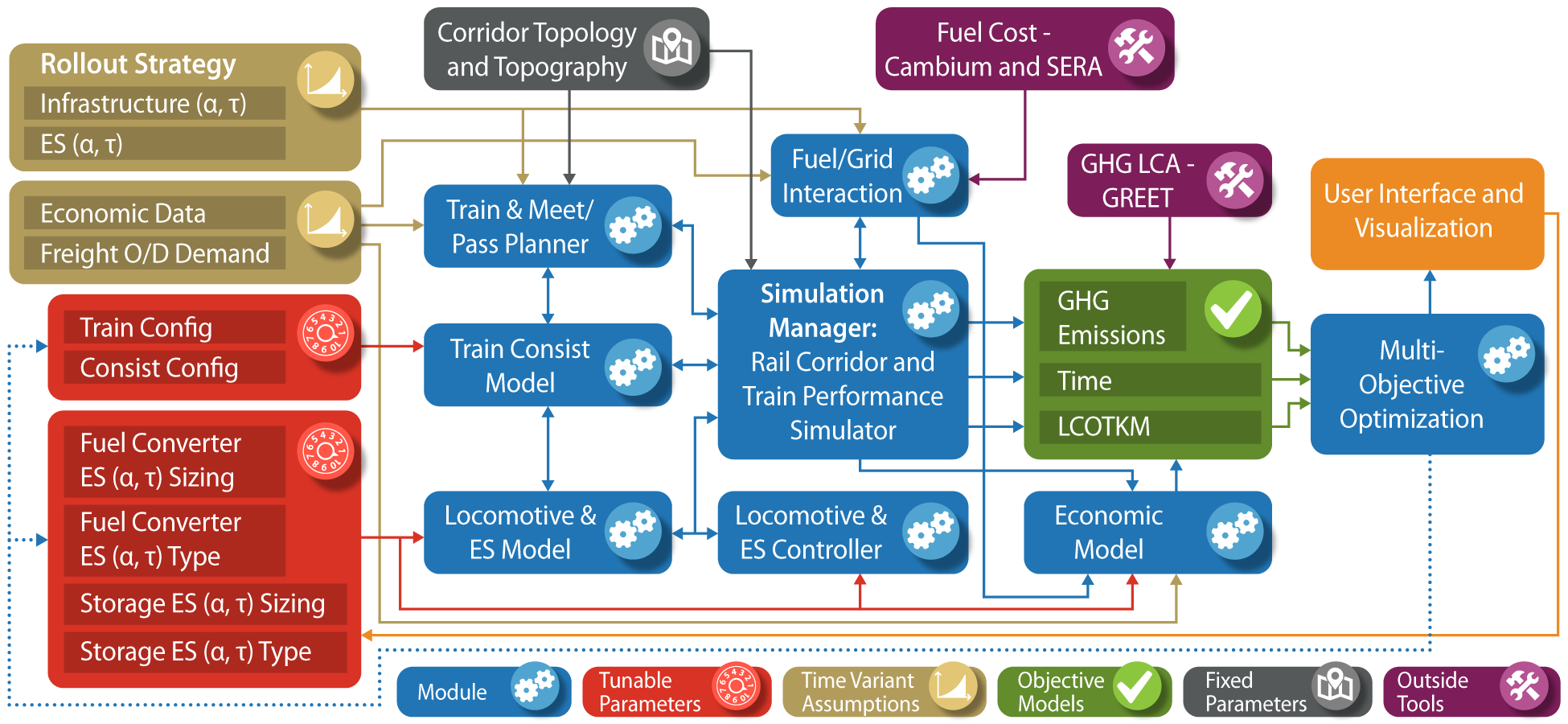
The Advanced Locomotive Technology and Rail Infrastructure Optimization System (ALTRIOS) is a unique, fully integrated, open-source software tool to evaluate strategies for deploying advanced locomotive technologies and associated infrastructure for cost-effective decarbonization. ALTRIOS simulates freight-demand driven train scheduling, mainline meet-pass planning, locomotive dynamics, train dynamics, energy conversion efficiencies, and energy storage dynamics of line-haul train operations. Because new locomotives represent a significant long-term capital investment and new technologies must be thoroughly demonstrated before deployment, this tool provides guidance on the risk/reward tradeoffs of different technology rollout strategies. An open, integrated simulation tool is invaluable for identifying future research needs and making decisions on technology development, routes, and train selection. ALTRIOS was developed as part of a collaborative effort by a team comprising The National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign (UIUC), Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), and BNSF Railway.
Much of the core code in ALTRIOS is written in the Rust Programming Language to ensure excellent computational performance and robustness, but we've built ALTRIOS with the intent of users interacting with the code through our feature-rich Python interface.
Installation
If you are an ALTRIOS developer, see Developer Documentation. Otherwise, read on.
Python Setup
- Python installation options:
- Option 1 -- Python: https://www.python.org/downloads/. We recommend Python 3.10. Be sure to check the
Add to PATHoption during installation. - Option 2 -- Anaconda: we recommend https://docs.conda.io/en/latest/miniconda.html.
- Option 1 -- Python: https://www.python.org/downloads/. We recommend Python 3.10. Be sure to check the
- Setup a python environment. ALTRIOS can work with Python 3.9, or 3.10, but we recommend 3.10 for better performance and user experience. Create a python environment for ALTRIOS with either of two methods:
- Option 1 -- Python Venv
- Navigate to the ALTRIOS folder you just cloned or any folder you'd like for using ALTRIOS. Remember the folder you use!
- Assuming you have Python 3.10 installed, run
python3.10 -m venv altrios-venvin your terminal enviroment (we recommend PowerShell in Windows, which comes pre-installed). This tells Python 3.10 to use thevenvmodule to create a virtual environment (which will be ignored by git if namedaltrios-venv) in theALTRIOS/altrios-venv/. - Activate the environment you just created to install packages or anytime you're running ALTRIOS:
- Mac and Linux:
source altrios-venv/bin/activate - Windows:
altrios-venv/Scripts/activate.batin a windows command prompt or power shell orsource ./altrios-venv/scripts/activatein git bash terminal - When the environment is activated, your terminal session will have a decorator that looks like
(altrios-venv).
- Mac and Linux:
- Option 2 -- Anaconda:
- Open an Anaconda prompt (in Windows, we recommend Anaconda Powershell Prompt) and run the command
conda create -n altrios python=3.10to create an Anaconda environment namedaltrios. - Activate the environment to install packages or anytime you're running ALTRIOS: run
conda activate altrios.
- Open an Anaconda prompt (in Windows, we recommend Anaconda Powershell Prompt) and run the command
- Option 1 -- Python Venv
ALTRIOS Setup
With your Python environment activated, run pip install altrios.
Congratulations, you've completed installation! Whenever you need to use ALTRIOS, be sure to activate your python environment created above.
How to run ALTRIOS
With your activated Python environment with ALTRIOS fully installed, you can download the demo scripts to the current working directory inside of a demos/ folder with:
import altrios as alt
alt.copy_demo_files()
You can run the Simulation Manager through a multi-week simulation of train operations in by running python sim_manager_demo.py in demos/. This will create a plots/ subfolder in which the plots will be saved. To run interactively, fire up a Python IDE (e.g. VS Code, Spyder), and run the file. If you're in VS Code, you can run the file as a virtual jupyter notebook because of the "cells" that are marked with the # %% annotation. You can click on line 2, for example, and hit <Shift> + <Enter> to run the current cell in an interactive terminal (which will take several seconds to launch) and advance to the next cell. Alternatively, you can hit <Ctrl> + <Shift> + p to enable interactive commands and type "run current cell". There are several other python files in the demos/ folder to demonstrate various capabilities of ALTRIOS.
If you plan to modify the data used in the demo files, copy the data files to your local directory and load them from there, e.g.
res = alt.ReversibleEnergyStorage.from_file(
alt.resources_root() / "powertrains/reversible_energy_storages/Kokam_NMC_75Ah_flx_drive.yaml"
)
would become
res = alt.ReversibleEnergyStorage.from_file(
"./custom_battery.yaml"
)
Nearly every code object in ALTRIOS can be read from or written to common data formats. For more details, see the SerdeAPI trait documentation. All of the functions in the SerdeAPI are available through the python interface.
Acknowledgements
The ALTRIOS Team would like to thank ARPA-E for financially supporting the research through the LOCOMOTIVES program and Dr. Robert Ledoux for his vision and support. We would also like to thank the ARPA-E team for their support and guidance: Dr. Apoorv Agarwal, Mirjana Marden, Alexis Amos, and Catherine Good. We would also like to thank BNSF for their cost share financial support, guidance, and deep understanding of the rail industry’s needs. Additionally, we would like to thank Jinghu Hu for his contributions to the core ALTRIOS code. We would like to thank Chris Hennessy at SwRI for his support. Thank you to Michael Cleveland for his help with developing and kicking off this project.
About this book
This is the overall ALTRIOS documentation. We're working toward making this a fully integrated document that includes both the Python API and Rust core documentation.



