Bulk Hydrogen Storage Cost Model#
Storage Types#
H2Integrate models at least three types of bulk hydrogen storage technologies:
Underground Pipe Storage: Hydrogen stored in underground pipeline networks
Lined Rock Caverns (LRC): Hydrogen stored in rock caverns with engineered linings
Salt Caverns: Hydrogen stored in solution-mined salt caverns
These storage options provide different cost-capacity relationships suitable for various scales of hydrogen production and distribution.
Cost Correlations#
The bulk hydrogen storage costs are modeled as functions of storage capacity using exponential correlations:
where \(m\) is the useable amount of H₂ stored in tonnes.
Installed Capital Cost and Lifetime Storage Cost#
The figures below show how storage costs scale with capacity for different storage technologies:
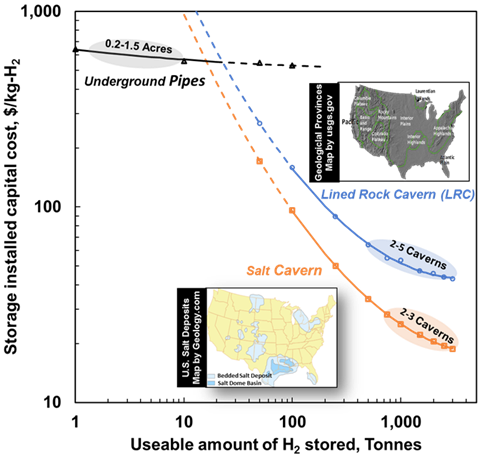
Figure 1a: Installed capital cost ($/kg-H₂) as a function of usable hydrogen storage capacity
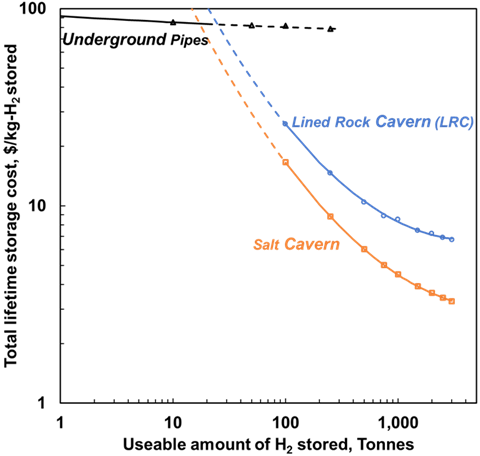
Figure 1b: Lifetime storage cost ($/kg-H₂-stored) as a function of usable hydrogen storage capacity
Cost Correlation Coefficients#
Capital Cost Coefficients (Figure 1a)#
Storage |
a |
b |
c |
|---|---|---|---|
Underground pipe storage |
0.004161 |
0.06036 |
6.4581 |
Underground lined rock caverns |
0.095803 |
1.5868 |
10.332 |
Underground salt caverns |
0.092548 |
1.6432 |
10.161 |
Annual Cost Coefficients (Figure 1b)#
Storage |
a |
b |
c |
|---|---|---|---|
Underground pipe storage |
0.001559 |
0.03531 |
4.5183 |
Underground lined rock caverns |
0.092286 |
1.5565 |
8.4658 |
Underground salt caverns |
0.085863 |
1.5574 |
8.1606 |